Definition
An Agent Node is an "intelligent decision-making + tool invocation" component designed to enable a Large Language Model (LLM) within a workflow to autonomously select and utilize tools at runtime based on defined strategies, facilitating multi-step reasoning or operations.
- By mounting a specific "Agent Strategy", the model can leverage contextual instructions, tool information, and its own reasoning results to determine in each execution round whether and how to employ a tool (system tools, cloud-side tools, etc). It then incorporates the data returned from these tools into the next round of reasoning or output, allowing for a more flexible processing flow.
- Compared to LLM nodes that utilize simple prompts, an Agent Node can engage in multiple cycles of "thinking and executing" according to the strategy, making it suitable for scenarios that require external data or executable actions.
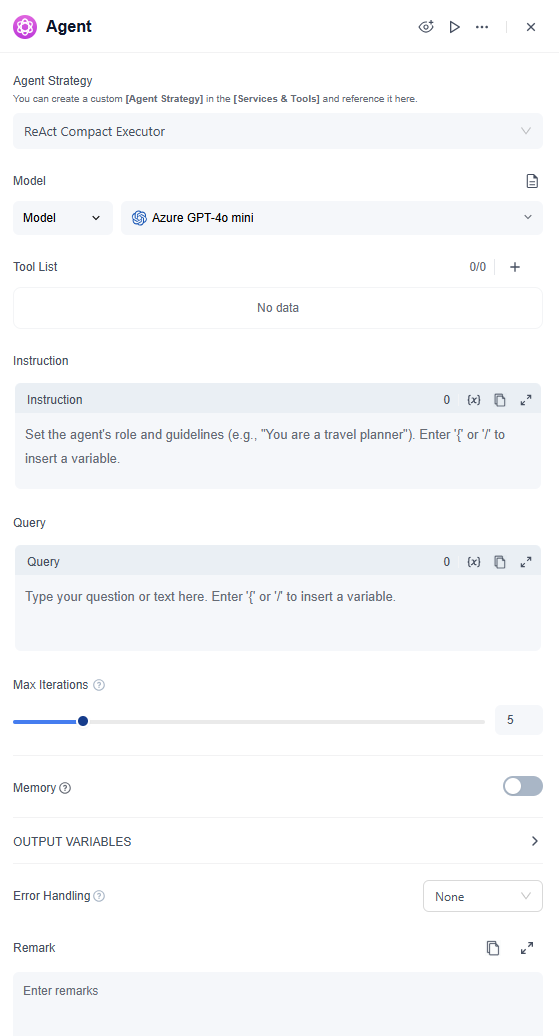
Add an Agent Node
- 1. Open the Workflow Editor
- Navigate to the workflow canvas you need to edit within the GoInsight.AI workspace.
- 2. Drag and Drop the Node
- Locate the "Agent" node in the left or top component panel on the canvas. Drag it to the appropriate position in the visual flowchart, connecting it with the preceding and subsequent nodes.
- 3. Select an Agent Strategy
- In the configuration panel of the Agent Node, specify an "Agent Strategy" that defines how the model will perform multi-step reasoning, invoke tools, and produce results.
- GoInsight.AI provides two default sources of Agent Strategies:
- Official System Strategy: Developed and embedded by the GoInsight.AI official team, suitable for common multi-step reasoning or tool-use scenarios.
- Custom Agent Strategy: Enterprise teams can create and publish their own agent strategy in the Services & Tools module.
Configure Node Parameters
Depending on the selected Agent Strategy, the Agent Node will display various parameters or functional options. Here are some common configurations:
- 1. Model
- Specify the Large Language Model used to drive the Agent (e.g., a model instance you have already configured in GoInsight.AI).
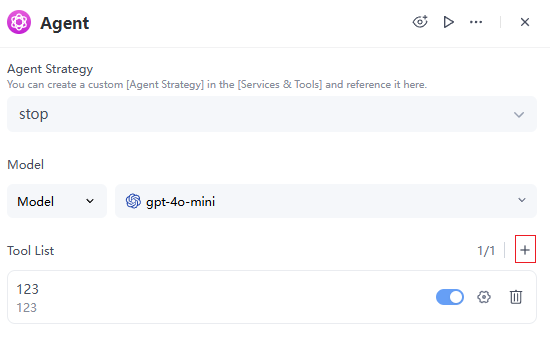
- 2. Tools
- Add or manage external capabilities that the Agent can invoke in the "Tools" section (such as HTTP requests, database queries, search plugins, etc.).
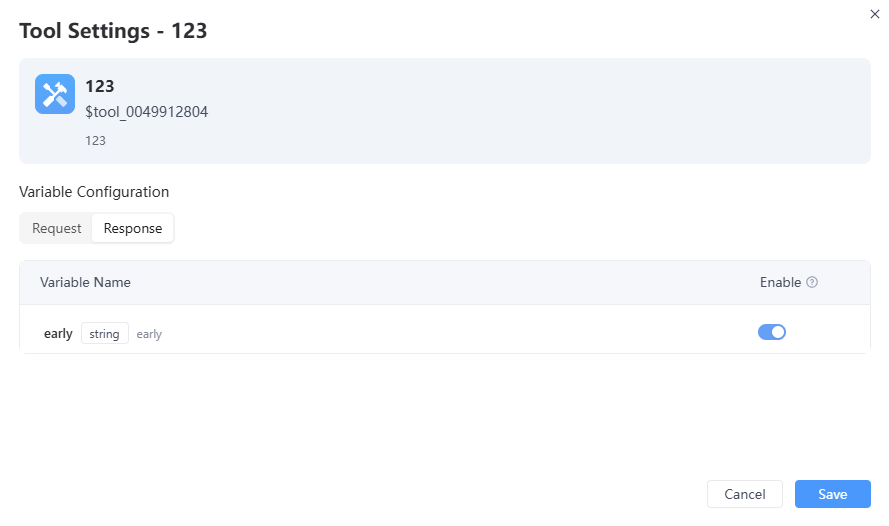
- If certain tools or plugins are already installed, click "+" to add them. You can enable/disable or delete added tools.

- You can also edit the tool’s specific settings: enable or disable input/output parameters. If you disable the relevant parameters, the corresponding results will not be passed to or returned to the LLM.

- When adding a tool, you can provide authorization information (such as API keys or access tokens) and include a description to help the model understand the tool’s functionality and invocation scenarios.
- 3. Instruction
- Used to inform the Agent of the context, objectives, or constraints.
- You can include "Role Setting," "Task Requirements," or "Business Context" in this section, ensuring the Agent adheres to these guidelines during multi-step reasoning.
- 4. Query
- Typically corresponds to user input or requirement text supplied from upstream nodes.
- The Agent will perform reasoning and generate action plans or tool invocation instructions by combining the Query and Instruction.
- 5. Max Iterations
- To prevent the Agent from looping indefinitely in multi-step reasoning, you can set a maximum execution count (iteration limit).
- If the Agent exceeds this count without concluding, it will automatically stop to avoid infinite invocation rounds.
- 6. Memory
- When memory is enabled, the Agent Node can retain context across multiple rounds of conversation or repeated command invocations, thereby generating coherent responses.
- History: The size of the “history” can be set using a slider or numerical value, indicating how many historical interactions the Agent Node can trace back and reference.
- Contextual Coherence: After enabling memory, the Agent Node can correctly understand subsequent mentions of pronouns, field names without explicit references, etc., by combining them with previous content.
- Accuracy and Performance: A larger memory window may result in higher model overhead, so it is necessary to balance actual needs with invocation costs.
- Memory Scope: Set the memory scope to Session or This node.
- 7. Output Variable
- Define the final output data structure of the Agent Node, enabling results to be passed to subsequent nodes for further processing.
- This includes the final response text, tool invocation results, or key information related to multi-round reasoning.
- 8. Error Handling
- Mechanisms triggered when a node fails, including:
- None: When a node fails, an error is reported and the workflow is terminated.
- Default Value: When a node fails, the process continues and uses the default value you specified as the output result.
- Error Branch: When a node fails, the workflow interrupts the current path and switches to the error handling branch you set.
View Execution Logs
The Agent Node generates detailed logs during execution to help you debug and understand the model's reasoning process and tool invocation trajectory:
- 1. Basic Information
- Displays the input, output, execution time, token consumption, etc. for each run.
- 2. Detailed Round Records
- You can view the Agent Node’s thinking, tool invocation, receiving tool responses, continued reasoning, etc., helping you analyze whether the reasoning logic and tool usage meet expectations.
- 3. Error Diagnosis
- If the Agent Node encounters invocation failures, timeouts, or other exceptions, the specific reasons will also be shown in the logs.
Developing and Managing Agent Strategy
If the built-in system strategies cannot meet specific customization needs, enterprises can also develop and publish their own custom agent strategy.
For more details, please refer to: Agent Strategy
Summary
- Agent Nodes empower large language models within workflow executions with "multi-step decision-making" and "self-service tool selection" capabilities, effectively addressing complex scenarios that simple dialog nodes cannot handle.
- You can flexibly combine models, tools, and strategies during node configuration and enhance contextual coherence and process transparency through memory and logging functions.
- If the default strategies do not meet business requirements, custom strategies can be created in the Services & Tools module to develop intelligent workflows better tailored to specific enterprise or scenario needs.
Leave a Reply.