- 1. Understanding the Basics of Building an AI Agent
- 2. 3 Methods to Create an AI Agent
- Build from Scratch
- Use an Existing AI Agent Framework
- Use a Workflow Automation Tool
- 3. How to Build an AI Agent without Code using GoInsight.AI
- Prerequisite:
- Step 1: Create Your Workflow
- Step 2: Configure the Workflow
- Step 3: Debug and Preview
- Step 4: Publish Your AI Agent
- 4. Conclusion
- 5. FAQs
Ever wished you had a smart assistant that could research, plan, and even get things done for you—without you lifting a finger? That’s exactly what AI agents can do. They’re not just chatbots; they can think, decide, and act on your behalf.
In this guide, we'll break down what an AI agent is, the basics and different ways to build one, and show you how to build an AI Agent using GoInsight.AI.
Understanding the Basics of Building an AI Agent
Before you start building your own AI agent, it’s helpful to understand the fundamental components that make it work. At a high level, an AI agent consists of several key parts that work together to perceive, think, and act.
● Environment: This is where your agent operates — it could be a chat interface, an app, or a set of APIs.
● Input/Perception: The way the agent receives information. This might be user text, data from websites, or signals from other systems.
● Reasoning & Decision Making: The “brain” of the agent, usually powered by large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, which processes inputs and figures out the next steps.
● Actions: These are the tasks the agent performs — sending messages, querying databases, calling APIs, or triggering workflows.
● Memory: Some agents keep track of previous interactions or context, allowing them to provide more coherent and personalized responses.
Think of it like a continuous loop: your agent listens, thinks, and does — over and over — to accomplish goals with minimal human intervention.
Technically, to build such an agent, you need:
● Access to an LLM (like OpenAI’s GPT models)
● A way to connect the model with tools and data sources
● Logic to decide what the agent does next
● Optionally, memory management to keep context
3 Methods to Create an AI Agent
There are several ways to build an AI agent, depending on your skills, resources, and goals. Let’s explore the three main approaches:
1. Build from Scratch
This approach involves designing and coding your AI agent entirely on your own. You directly interact with language model APIs (like OpenAI’s GPT), implement the logic for how the agent interprets inputs, makes decisions, and manages memory. You also handle integration with external services, databases, or tools. Essentially, you build every component from the ground up, tailoring the agent’s behavior exactly to your needs.
Pros
- Full control over every detail
- Can be optimized for specific needs
- No dependency on third-party platforms
Cons
- Requires strong programming and system design skills
- Time-consuming to build and maintain
- You must handle infrastructure and deployment yourself
2. Use an Existing AI Agent Framework
Frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, or CrewAI provide a set of reusable building blocks and abstractions for building AI agents. They simplify complex tasks such as memory management, chaining multiple prompts, tool integration, and multi-agent coordination. You write code to customize and assemble these components into an agent, which speeds up development and helps avoid reinventing the wheel.
Pros
- Saves development time with reusable modules
- Flexible and customizable to your use case
- Large communities and documentation for support
Cons
- Still requires programming knowledge
- Some frameworks have a learning curve
- Limited by framework design and updates
3. Use a Workflow Automation Tool
Low code platforms let you build AI agents visually by connecting components such as language models, APIs, and logic blocks through drag-and-drop interfaces. Minimal or no coding is required. These tools often include workflow scheduling, multi-step automation, and easy integrations, making them perfect for non-developers or teams seeking fast prototyping without managing complex code.
Pros
- Beginner-friendly; minimal to no coding needed
- Rapid prototyping and easy iteration
- Seamless integration with other business tools and APIs
- Great for collaboration across teams
Cons
- May not support highly complex or custom logic
- Potential vendor lock-in
- Less control over performance optimization
Each method has its place, and your choice depends on your technical background, project requirements, and timeline.
How to Build an AI Agent without Code using GoInsight.AI
GoInsight.AI stands out as a platform for building AI agents by seamlessly combining powerful AI models with visual low-code workflows. Unlike typical automation tools, it lets you orchestrate multiple leading LLMs, integrate knowledge retrieval (RAG), and enable multi-agent collaboration—all within one secure, enterprise-ready environment.
In this tutorial, we’ll create a hands-on industry insight assistant that gathers data and delivers concise market summaries automatically.
Prerequisite:
Before you start building this workflow, make sure you have:
● Access to the GoInsight.AI platform.
● A valid NewsAPI account and API key (you can get one at newsapi.org).
● Basic familiarity with setting up nodes and variables (don’t worry, no advanced coding is required).
Step 1: Create Your Workflow
Log in to GoInsight.AI, go to “InsightFlow” and click “+ New Workflow”. Choose the type “Interactive Flow”, give it a name, and you’ll land in the workflow canvas.
By default, an interactive flow starts with Start → LLM → Answer. For our use case, we’ll expand it by adding:
● A Code node to calculate a date range
● A HTTP Request node to pull news data
● Another Code node to process that data before sending it to the LLM
Step 2: Configure the Workflow
Now that the workflow structure is in place, it’s time to bring each node to life. Think of this as wiring the logic so your AI agent knows where to fetch data, how to process it, and how to deliver the answer.
1. Start Node – Capture the User’s Question
No special setup needed here—just use the built-in system variable Query to capture whatever the user asks. This becomes the foundation for all the following steps.
2. Code Node – Define a Time Range
Before fetching data, we’ll limit the search to a specific period to avoid pulling in massive, irrelevant datasets.
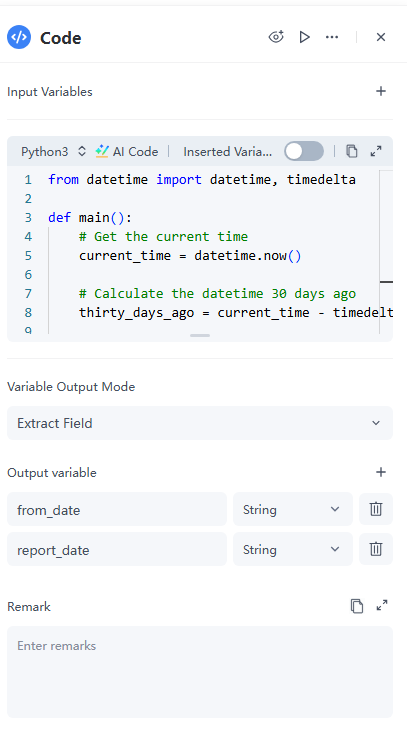
● Input Variables: None.
● Python: Here’s sample code for a 30-day range. You can change the fields for a different period, but keep them consistent. If you can’t code, click “AI Code”, describe your needs, and it will generate the code.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def main():
# Get the current time
current_time = datetime.now()
# Calculate the datetime 30 days ago
thirty_days_ago = current_time - timedelta(days=30)
# Format the datetime for NewsAPI's 'from' parameter (YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS)
formatted_from_date = thirty_days_ago.strftime('%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S')
# New: Current date for report display (YYYY-MM-DD)
report_date = current_time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# Return a dictionary containing the variables to be passed to the next nodes
return {
"from_date": formatted_from_date, # Output variable for NewsAPI's 'from' parameter
"report_date": report_date # Output variable for the report's current date
}● Output Variables: from_date and report_date (both String).
3. HTTP Request Node – Fetch Industry News
Here’s where the AI agent reaches out to a data source. We’ll connect to NewsAPI to get the latest articles related to the user’s keywords.
● First, register with NewsAPI to get your API key. After you get it, copy and save it for later use.
● Then, go back to GoInsight.AI and enter the following configuration.
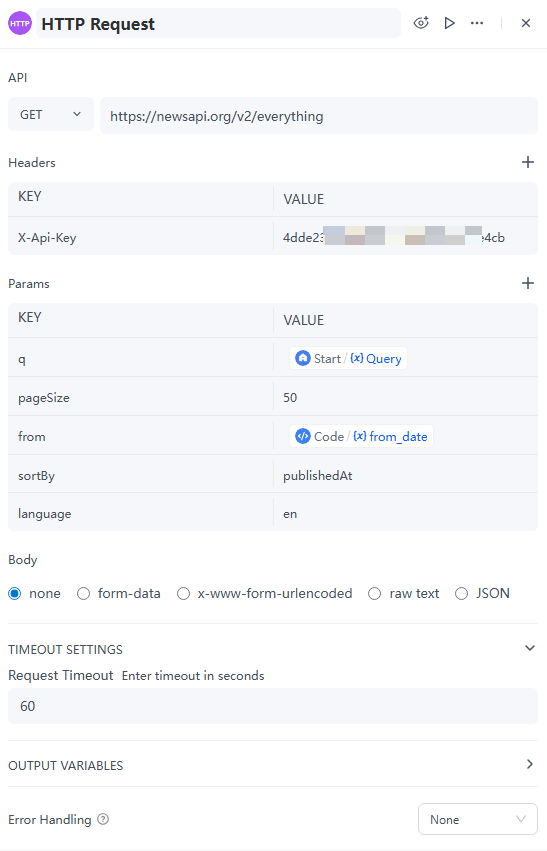
4. Code Node – Clean and Format the Data
Raw API responses are messy. This step filters out unnecessary fields, extracts the useful text, and merges them into a clean string.
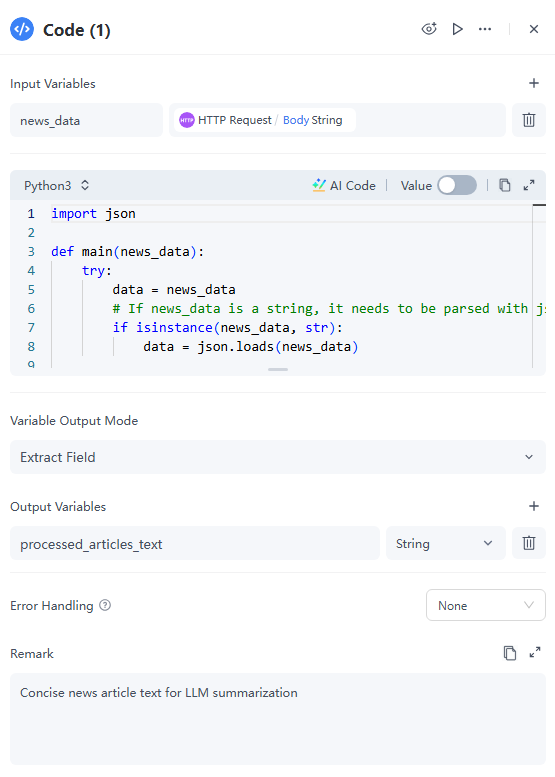
● Input Variables: Set the variable name to news_data and assign it the output from the previous node — {{HTTP_Request.Body}}.
● Python: Example code below.
import json
def main(news_data):
try:
data = news_data
# If news_data is a string, it needs to be parsed with json.loads()
if isinstance(news_data, str):
data = json.loads(news_data)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# If parsing fails, return a specific error message
return {"processed_articles_text": "Error: Could not parse news data as JSON."}
except TypeError:
# If news_data is not valid (e.g., None), return an error
return {"processed_articles_text": "Error: news_data is not valid."}
processed_articles = []
# Check if 'articles' key exists and its value is a list (this is NewsAPI's structure)
if data and 'articles' in data and isinstance(data['articles'], list):
for article in data['articles']:
title = article.get('title', '')
description = article.get('description', '')
url = article.get('url', '') # Ensure URL is extracted
# Filter out articles with empty titles or descriptions to ensure meaningful content for the LLM
# Ensure URL is also present, as it's useful for the report
if title and description and url:
# IMPORTANT CHANGE HERE: Include the link in a Markdown link format
# LLMs generally understand and preserve this format well.
combined_text = f"Title: {title}\nDescription: {description}\n[Source Link]({url})"
processed_articles.append(combined_text)
if not processed_articles:
return {"processed_articles_text": "No valid articles found after processing NewsAPI response."}
# Concatenate the processed articles into a single string, separated by a distinct delimiter.
# Limit the number of articles (e.g., top 20) to prevent the LLM input from becoming too long.
return {"processed_articles_text": "\n\n---\n\n".join(processed_articles[:20])}● Output Variables: Set as processed_articles_tex (String).
5. LLM Node – Generate the Market Insight
The heart of the AI agent. This is where the data turns into a readable, insightful summary.
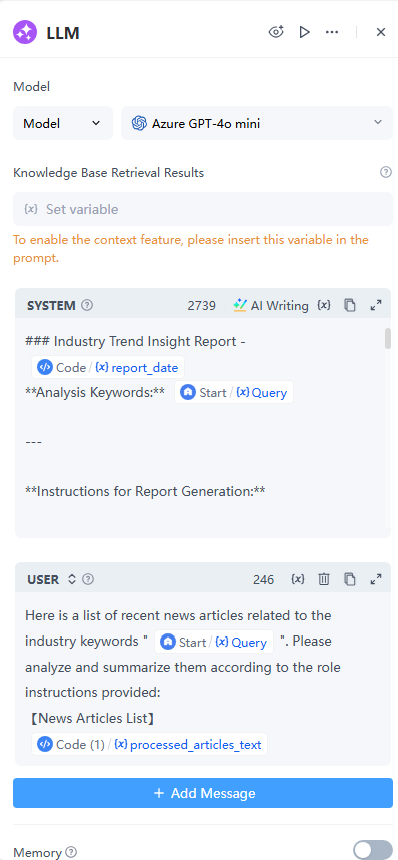
● Model: Here we choose Azure GPT-4o mini.
● SYSTEM: Sets the AI’s role and style of output. The more structured your instructions, the better the results. Here is an example:
### Industry Trend Insight Report - {{Code.report_date}}
**Analysis Keywords:** {{Start.Query}}
---
**Instructions for Report Generation:**
You are an expert industry analyst. Your task is to generate a comprehensive "Industry Trend Insight Report" based on the provided news articles. Adhere strictly to the following structure and guidelines:
**Output Structure:**
#### 1. Key Trends Summary
- **Trend Name:** [Identify a concise trend name]
- **Core Content:** [Summarize the main content of the trend based on the articles. Ensure this is direct and informative.]
- **Key Events/News:** [Mention specific events or news items that support this trend. **For each event/news mention, if a source link is available within the provided articles (e.g., "[Source Link](URL)"), incorporate this exact Markdown link directly into the report after the relevant detail.**]
- **Potential Impact:** [Analyze the potential implications or future developments related to this trend.]
#### 2. Key Company/Product Developments
- [Identify specific companies or products mentioned in the news articles that highlight significant developments. **For each company/product development, if a source link is available, include this exact Markdown link.**]
#### 3. Potential Risks & Opportunities
- **Risks:** [Identify potential risks related to the overall industry or trends based on the articles.]
- **Opportunities:** [Identify potential opportunities arising from the trends or developments.]
**Important Guidelines:**
* **Data Source:** All information, analyses, and summaries must be strictly derived from the `【News Articles List】` provided below.
* **Source Link Integration:** When extracting `Key Events/News` or `Key Company/Product Developments`, if the original article's text contains a `[Source Link](URL)` format, **you MUST include this exact Markdown link within your report right after the relevant piece of information.** Do not modify the link format or content. If multiple sources support a single point, pick the most relevant one, or include a few if appropriate and concise.
* **Concise and Professional:** The language style should be professional, objective, and the report content should be concise and to the point.
* **English Report:** All content should be output in English.
* **No Fabrication:** Do not invent or fabricate any information not present in the provided articles.
* **Data Sufficiency:** If the provided news articles are insufficient to form a detailed analysis, or if no significant trends can be identified, state this clearly at the end. Otherwise, provide a concluding remark on sufficiency.
---
**【News Articles List】**
{{Code.processed_articles_text}}● USER: Passes in the processed articles and the original query. Here is an example:
Here is a list of recent news articles related to the industry keywords "{{Start.Query}}". Please analyze and summarize them according to the role instructions provided:
【News Articles List】
{{Code(1).processed_articles_text}}6. Answer Node – Deliver the Result
● Reply: Simply outputs the LLM’s generated text as the final answer to the user.
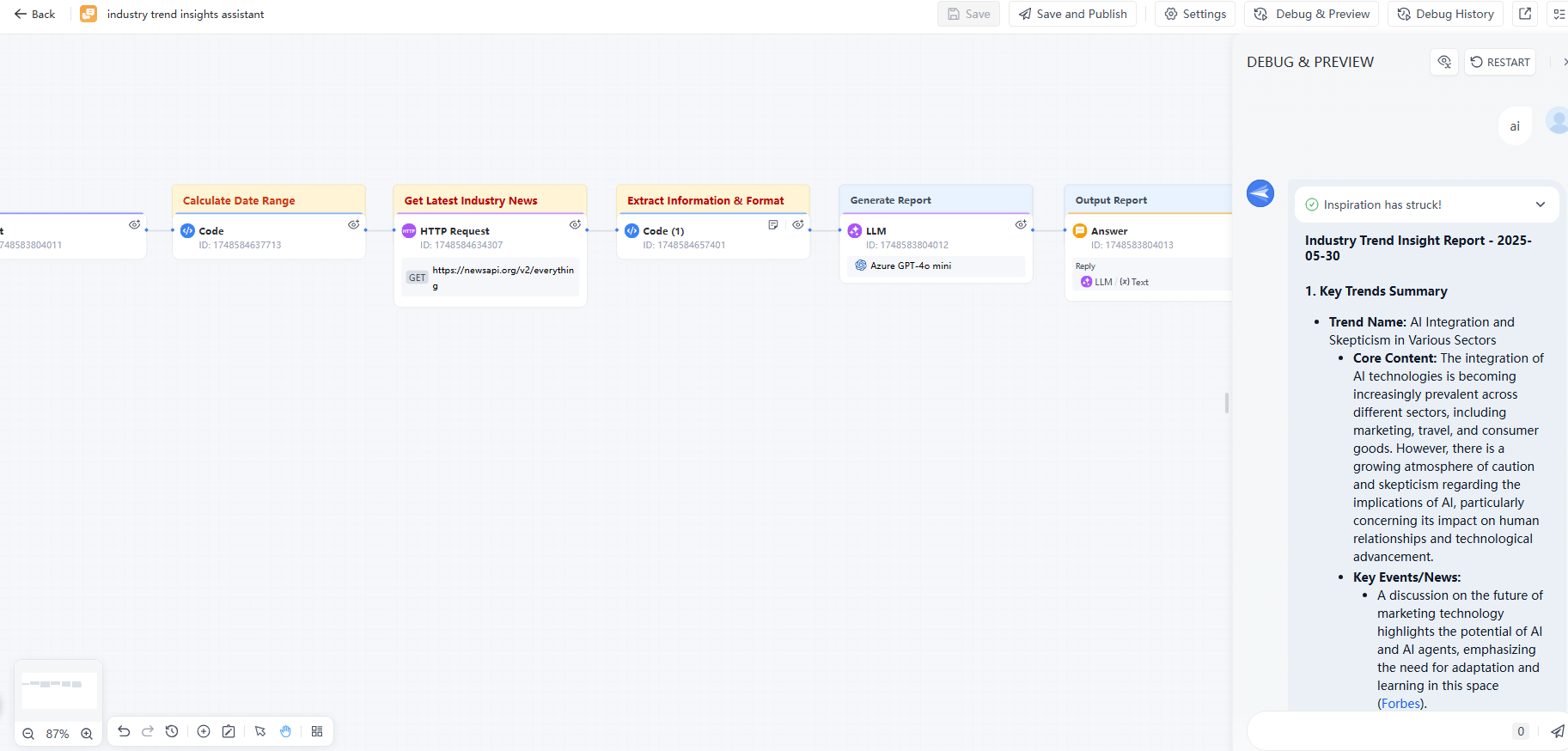
Step 3: Debug and Preview
Click Save, then Debug & Preview to see if the workflow works as expected. Adjust as needed until you’re happy with the output.
Step 4: Publish Your AI Agent
When everything looks good, hit Save and Publish. You can:
● Track published versions
● Share your AI agent as a bot
● Set security permissions
Copy the share link and your Industry Trend Insight Assistant is ready to use! You can also create more workflows tailored to your business needs, helping you or your team boost efficiency and achieve better results.
Conclusion
We started by breaking down what an AI agent really is and the essential building blocks behind it. Then, you learned there’s no single way to build—whether coding from scratch, using AI frameworks, or leveraging low-code platforms like GoInsight.AI, each path has its strengths.
Remember the key takeaways:
● AI agents revolve around perceiving, reasoning, acting, and remembering.
● Choose your creation method based on your goals and skills.
● Low-code platforms like GoInsight.AI dramatically speed up development while maintaining flexibility and control.
● Building an AI agent is not just technical—it's about unlocking new ways to solve problems efficiently.
Keep exploring, building, and iterating. The smarter your agent, the more impact it can make. If you’ve been wondering how to build an AI agent, now you have the knowledge and tools to start your journey with confidence.
FAQs
You can create an AI agent in 3 ways:
1. Code from scratch for full control.
2. Use AI frameworks like LangChain for faster development.
3. Leverage low-code platforms like GoInsight.AI for easy visual building without heavy coding.





Leave a Reply.