How to Integrate Free LLMs with PyCharm: A Practical Guide
PyCharm is a powerful IDE for Python programmers, and integrating LLMs can take its capabilities to the next level.
This guide provides an in-depth look at how to set up free LLM integrations, designed for first-time users who may not know what they are capable of or how to begin.
Before We Start, What Do You Need to Know?
What Are Free LLMs and How Can They Help?
A free Large Language Model (LLM) is an AI trained on text and code to understand natural language and generate useful responses.
While some advanced models offer free trials with usage limits, many free LLMs are available for developers to experiment with and integrate into their workflows. These models can be a great "coding sidekick" for testing new concepts.
Here are a few examples:
- Code Llama (Meta): specifically designed for coding
- Gemma (Google): light-weight, open-source LLM
- OpenRouter/Cloudflare AI: platforms where you can access and try various free models
LLMs are especially useful for coding tasks. They can help you with:
- Writing new code from plain-language descriptions.
- Automating repetitive tasks, like generating boilerplate code.
- Spotting potential bugs or suggesting fixes.
- Annotating and explaining code for better understanding.
- Transforming existing code into cleaner, more maintainable versions.
The main difference between free and paid LLMs is performance. Paid versions are usually smarter, faster, and more accurate, while free LLMs are perfect for experimentation or lightweight integration.
Why PyCharm is Perfect for This?
PyCharm is a very popular and powerful IDE for Python programmers, with a great set of features that make it ideal for integrating AI.
- Top-Tier Python Support: It makes Python development smooth with intelligent autocomplete, debugging tools, and code inspections.
- Plentiful Plugin Marketplace: You can easily extend its functionality with thousands of plugins, including those for AI integration.
- Versatile Environment Management: This feature streamlines dependency and configuration management, keeping your workspace neat.
- User-Friendly UI: It's easy for beginners to use and for advanced users to customize to their liking.
Simply put, PyCharm's powerful features and flexibility make it a great place to try out free LLM integrations.
How Do You Integrate an LLM into PyCharm?
There are two methods you can use to integrate an LLM into PyCharm: using plugins or a direct API connection.
Method 1: How to Get Started Quickly with a Plugin
The simplest way to bring AI to PyCharm is by using a plugin. This method is suitable for beginners, students, or users who prefer quick access to AI support without additional technical setup.
Since plugins are baked into the PyCharm ecosystem, installation is quick and straightforward, updates are automatic, and you can use AI features directly in the editor.
Step 1. Open the PyCharm Plugins Marketplace
1. Open PyCharm on your PC.
2. Go to the 'Plugins' tab on the left-hand menu bar.
Step 2. Install an AI Plugin
1. Select an AI plugin to install or type into the search bar for 'AI'. Some examples include:
- JetBrains AI Assistant
- CodeGPT
- ProxyAI
2. Click 'Install' on the Plugin page.
Step 3. Restart PyCharm
Once you install a plugin, PyCharm will prompt you to restart the software. Complete the restart.
Step 4. Configure the Plugin
1. Open a New Project on PyCharm.
2. On the right-hand menu bar, select your plugin. We're using 'ProxyAI' as an example.
3. Depending on your plugin, you may require an API key to use AI capabilities.
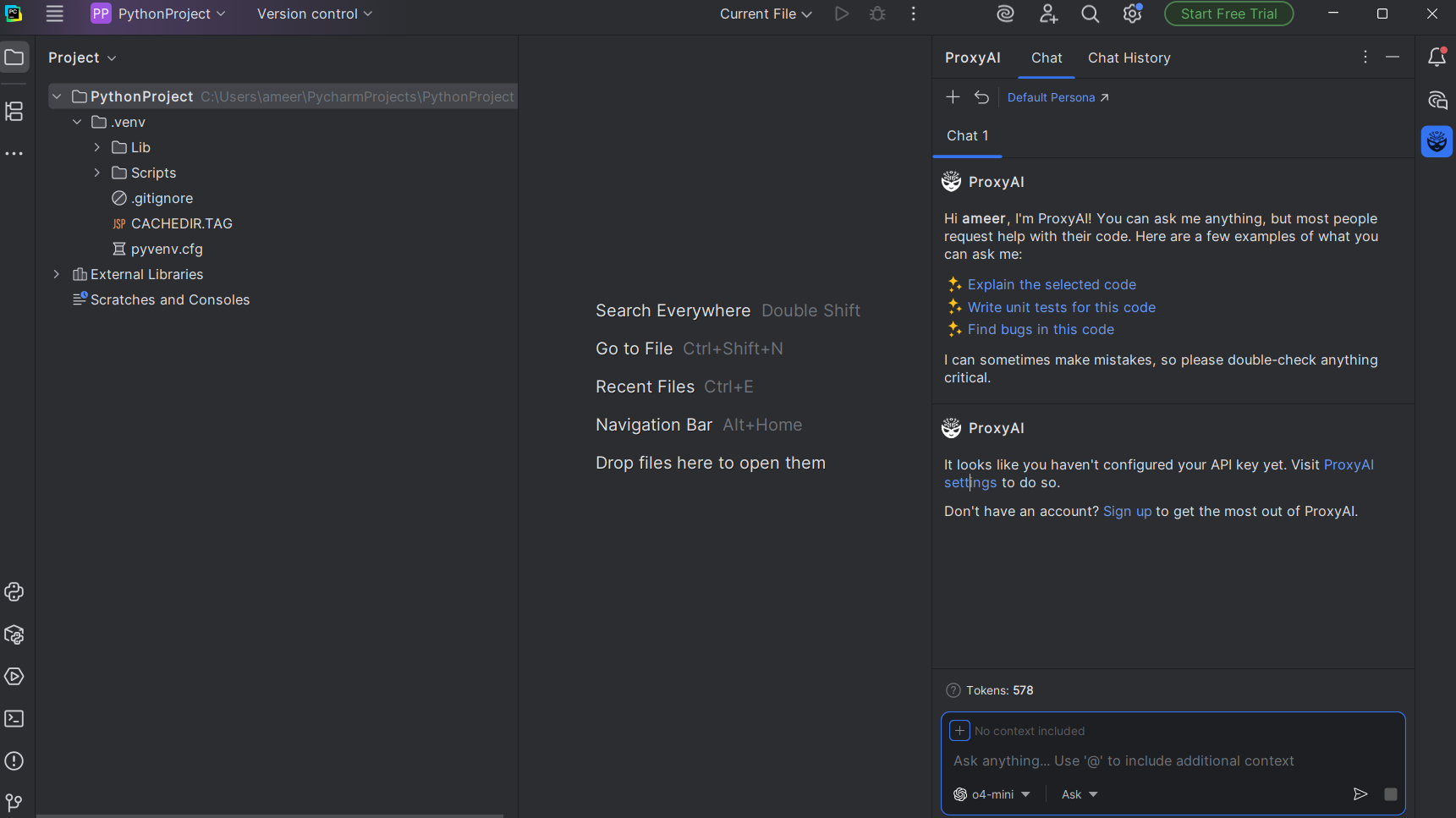
4. Click the 'ProxyAI settings' button or equivalent.
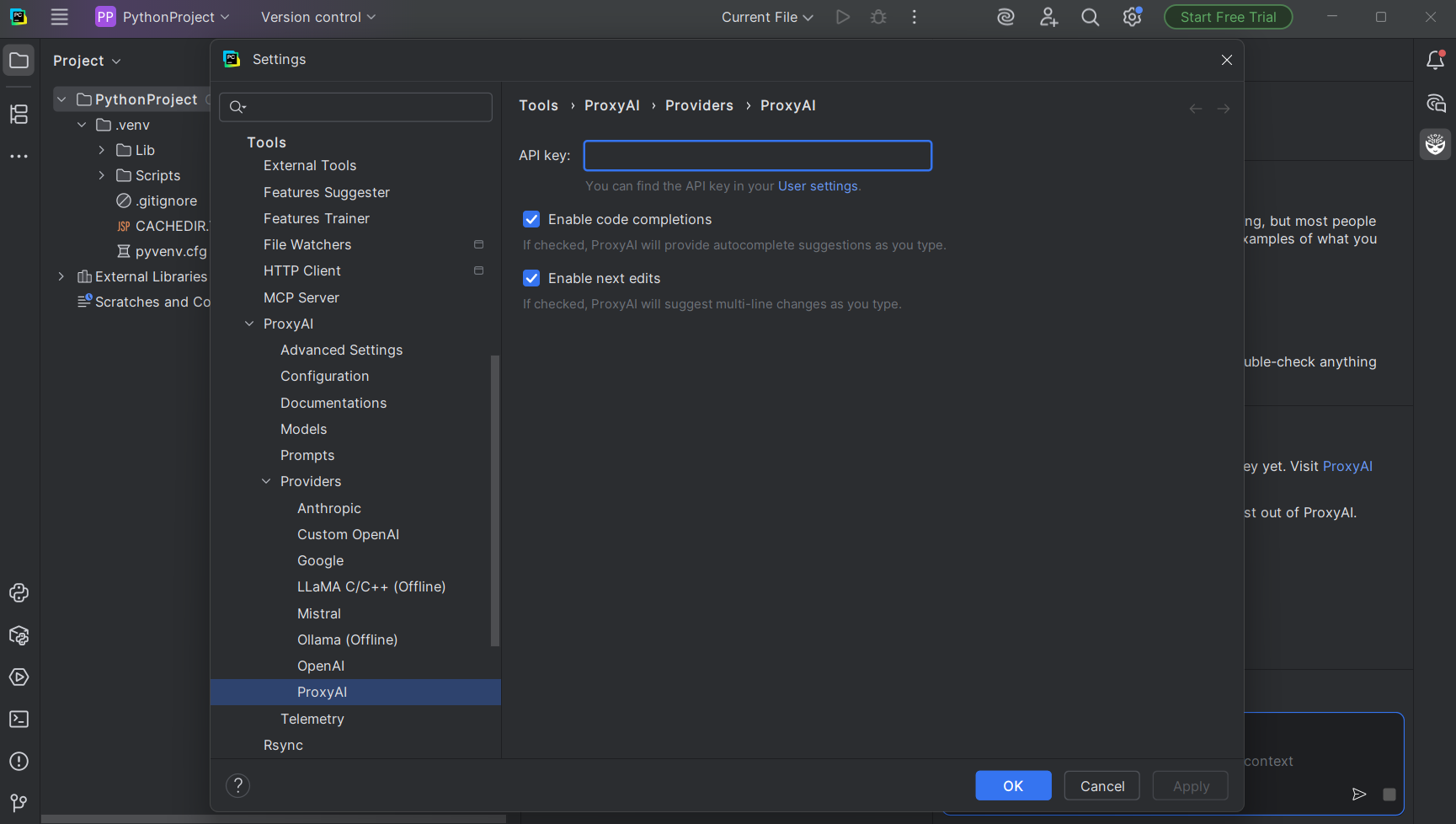
5. You'll be redirected to the plugin's settings page.
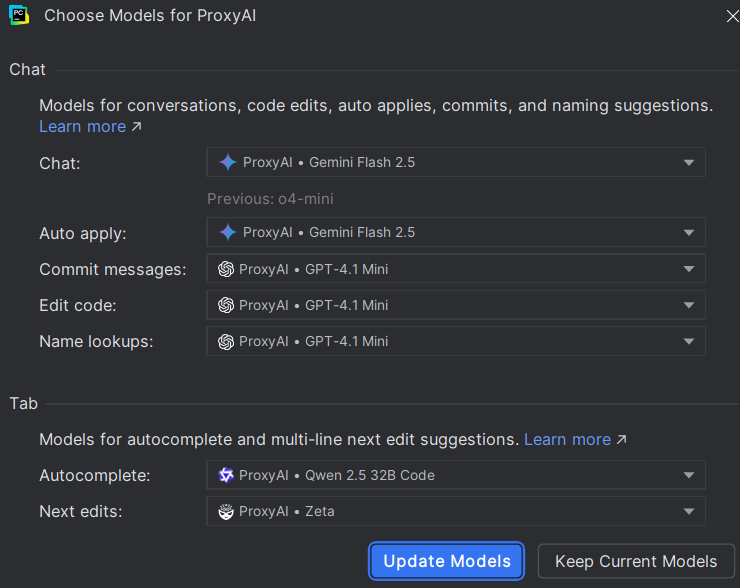
6. Paste the API key for your model of choice here. Ensure the model you use is supported by the plugin.
7. Complete the model setup for the plugin by clicking the 'Update Models' button.
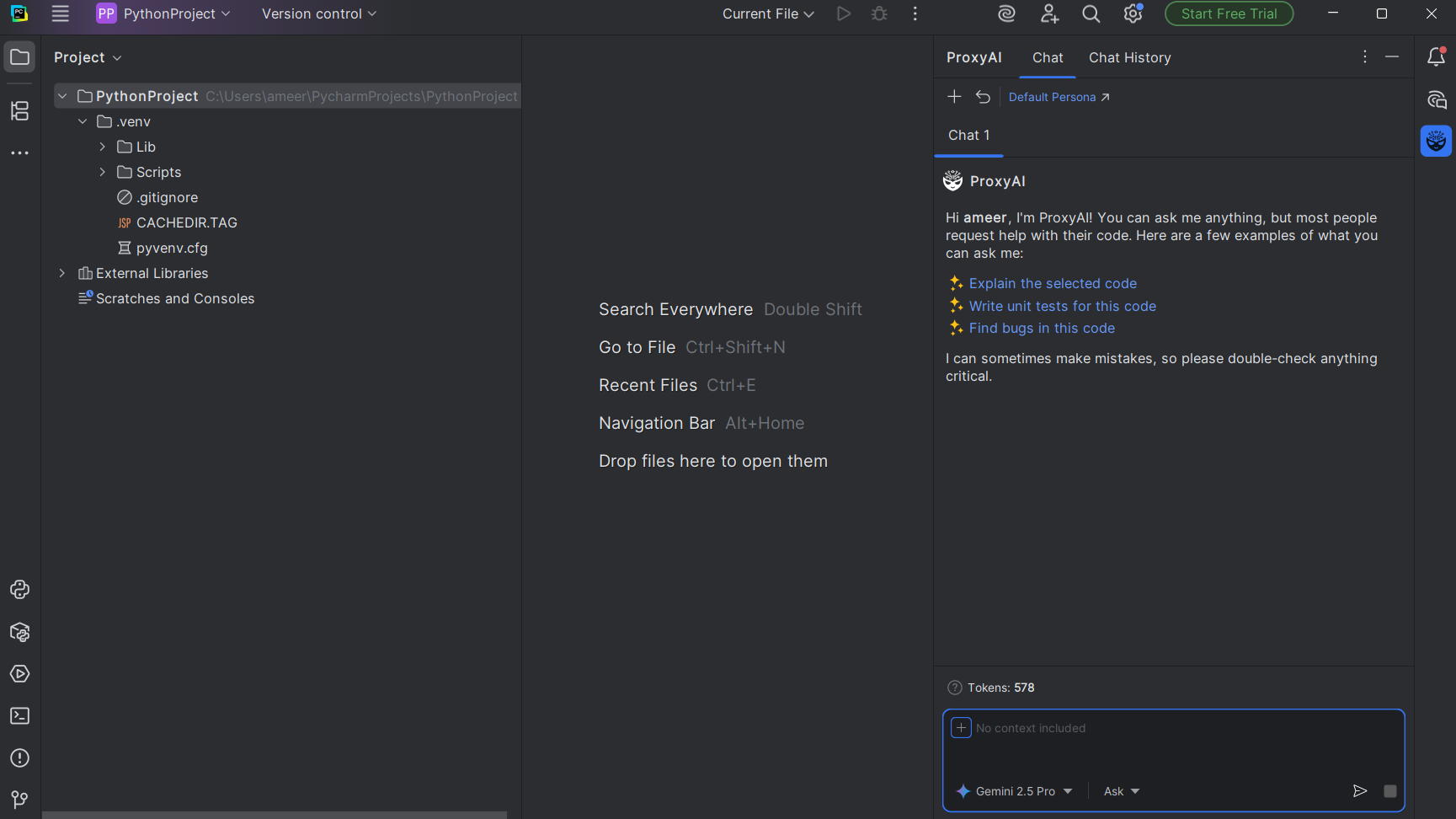
8. Open the plugin again and type into the text box on the right-hand side of the PyCharm page to use the AI.
Method 2: How to Use a Direct API Connection for More Flexibility
Alternatively, if you're a more advanced user and prefer more flexibility and control, connecting directly with an API is ideal.
This allows you to access different AI models, beyond what plugins have to offer, allowing you more customization options and the ability to fine-tune how the AI interacts with your coding projects.
However, it takes a bit more setup than downloading and installing a plugin as well as API access to the LLM you want to use.
Step 1. Get an API Key
First, you'll need to get a valid, working API key to get started. You can select your LLM model of choice to get an API key from your provider (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic, Cloudflare AI, Google Gemini, etc.).
The process of obtaining an API key may differ slightly depending on your provider. However, it typically follows the same steps as signing in to your account, generating a key, and copying it.
As long as you have a valid API key, the method we're showcasing here will work regardless of which LLM you're using.
For our example, we're using an API key from Google AI Studio, which you can get for free if you have a Google account:
1. Go to the Google AI Studio site.
2. Log in to your Google account. Consent to the pop-up to continue.
3. This will allow you to access Google's Gemini model. The screen should look like this:
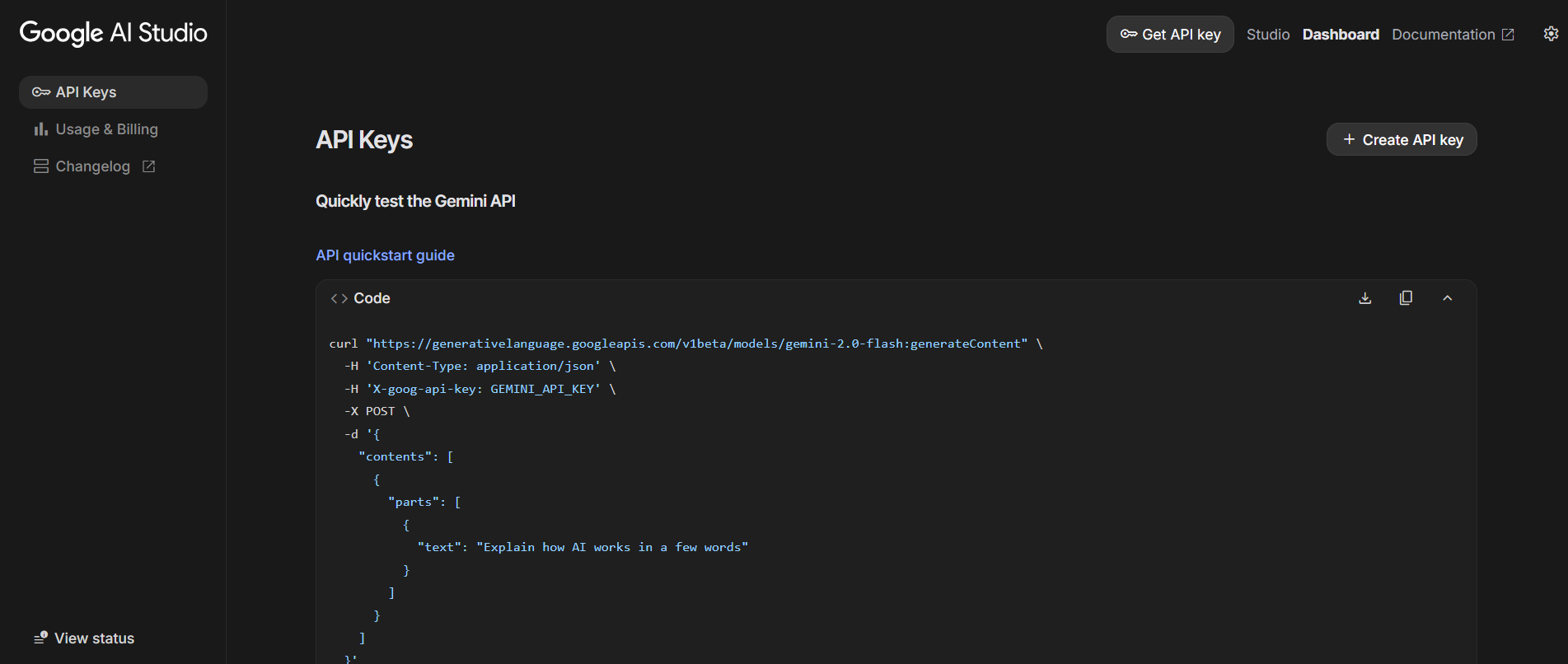
4. Now select the '+ Create API key' button.
5. In the 'Create API key' pop-up, click on the search bar under 'Search Google Cloud projects'.
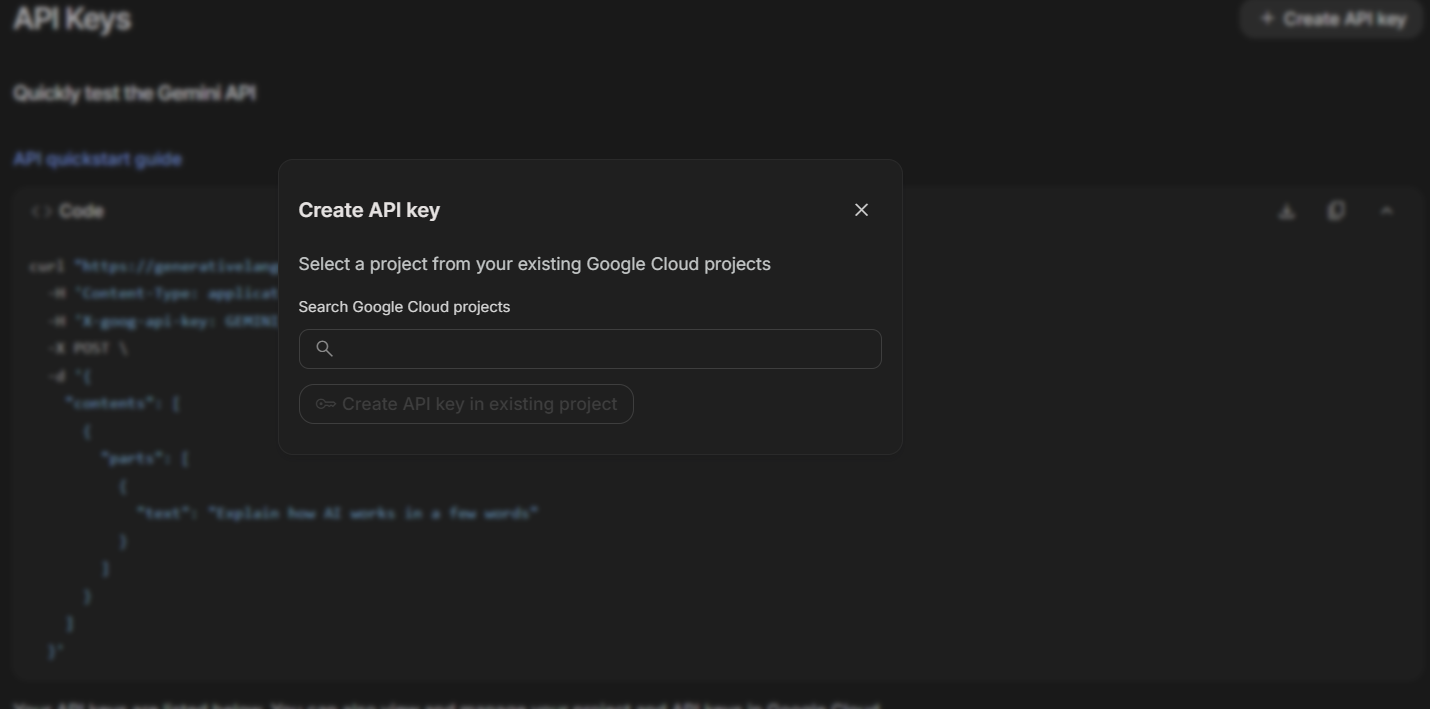
6. Select the model you'd like to generate an API key for.
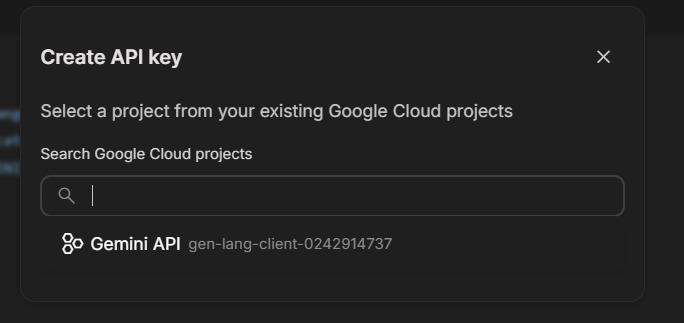
7. Click on the 'Create API key in existing project' button.
8. Copy the API key by clicking the 'Copy' button.
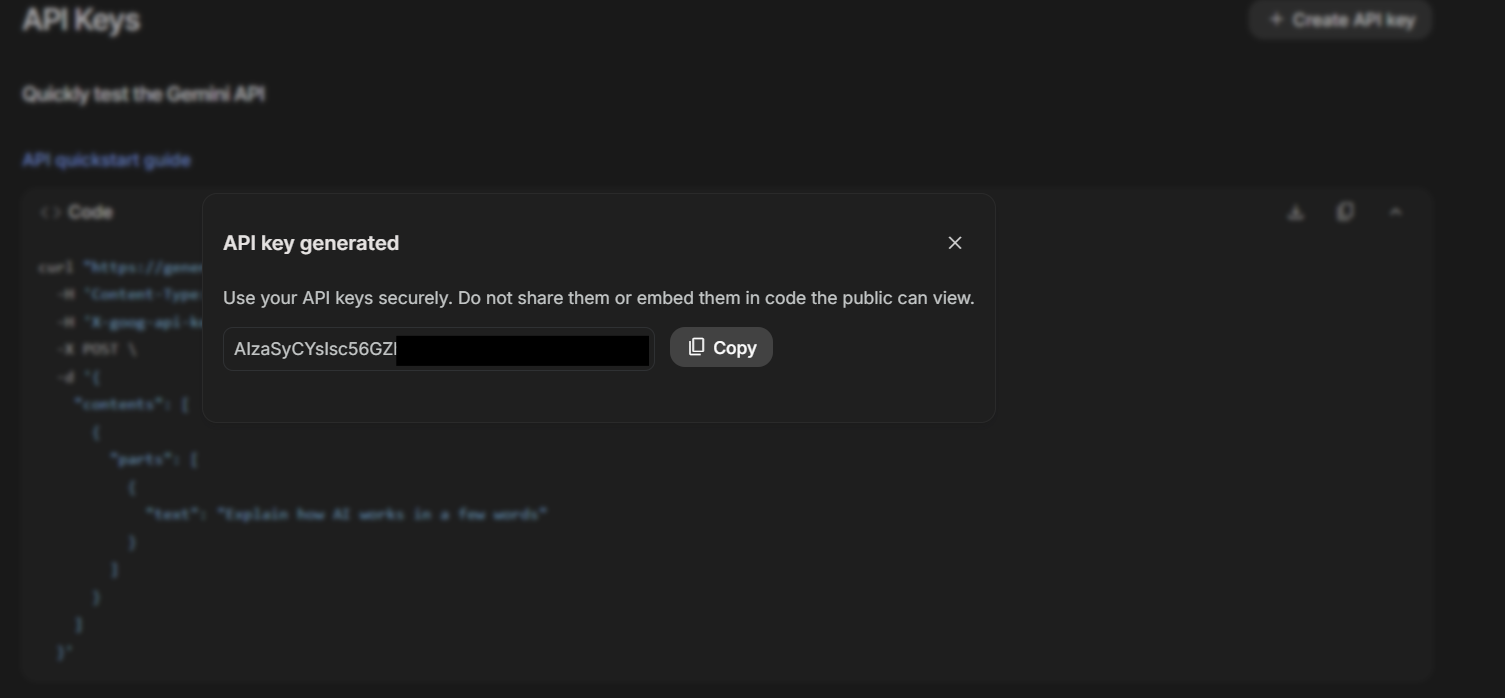
Step 2. Connect the API Key to PyCharm via Environment Variable
Now that you've got a working API key, the next step is to add it to PyCharm. There are a few ways of doing it, like using plugins, or PyCharm's AI Playground plugin, which allows you to add different LLM models to PyCharm natively.
However, AI Playground requires a 'Professional' subscription.
You can also add an API key to PyCharm's built-in configuration via an environment variable. This keeps your API key secure while being easily accessible for scripts.
Step 3. Open the Configurations Page
The method below will use the API key we've generated above and add it as an environment variable:
1. Open PyCharm and start a new project or open an existing project.
2. On the project page, open the 'Main Menu' by clicking the '≣' icon in the top left corner.
3. From the taskbar pop-up, select 'Run'.
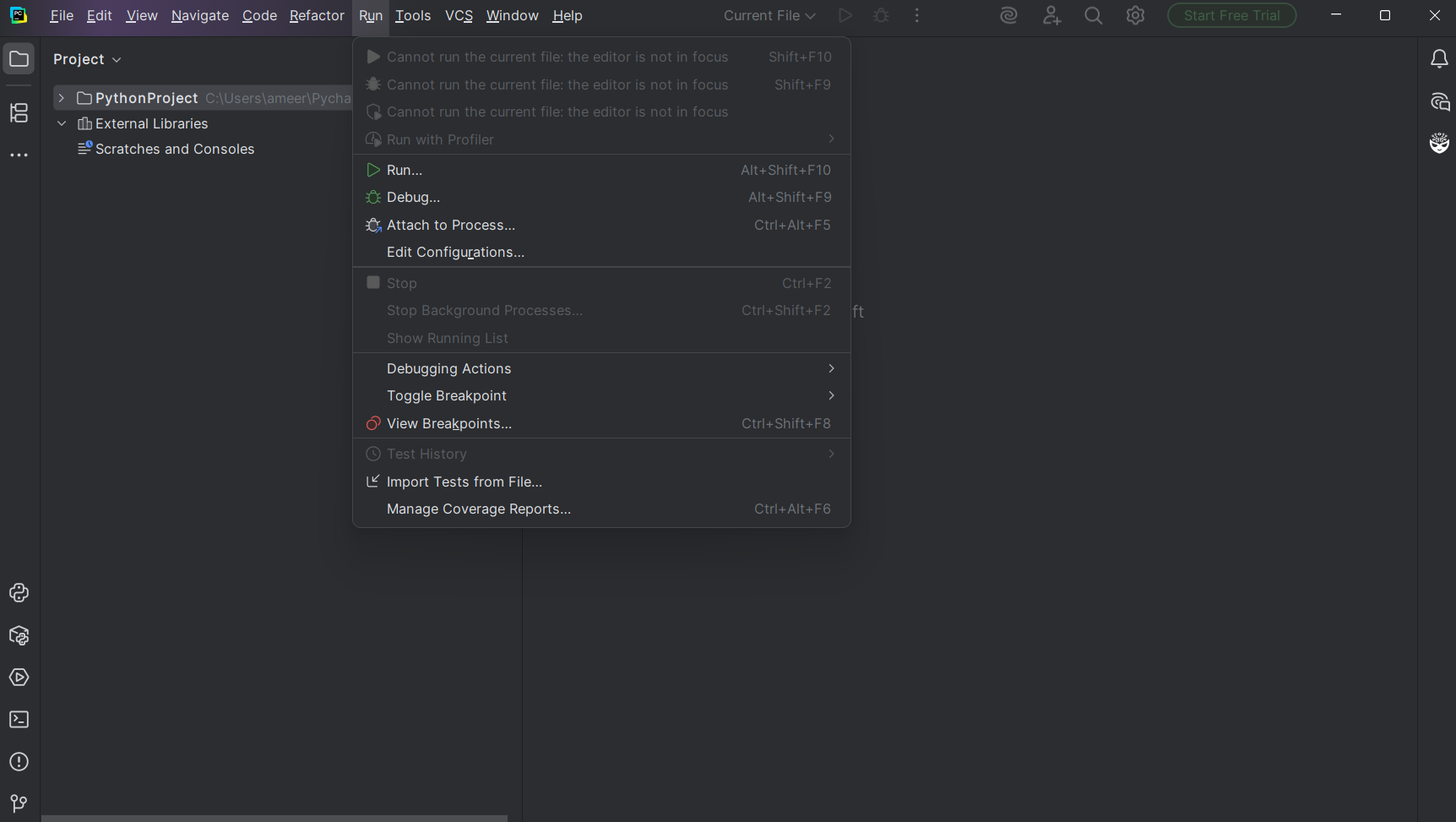
4. Select 'Edit Configurations…'
Step 4. Add a New Configuration
1. If the project already has a valid Python configuration, select it. Otherwise, click on 'Add new run configuration…'
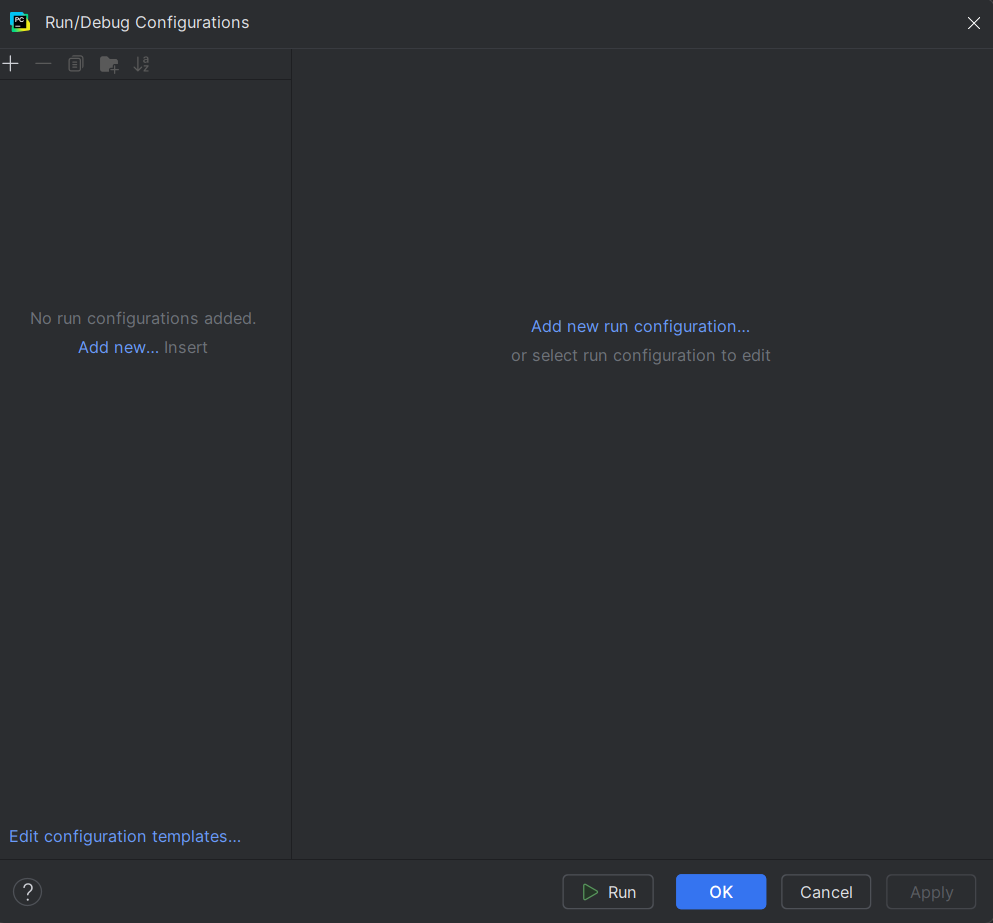
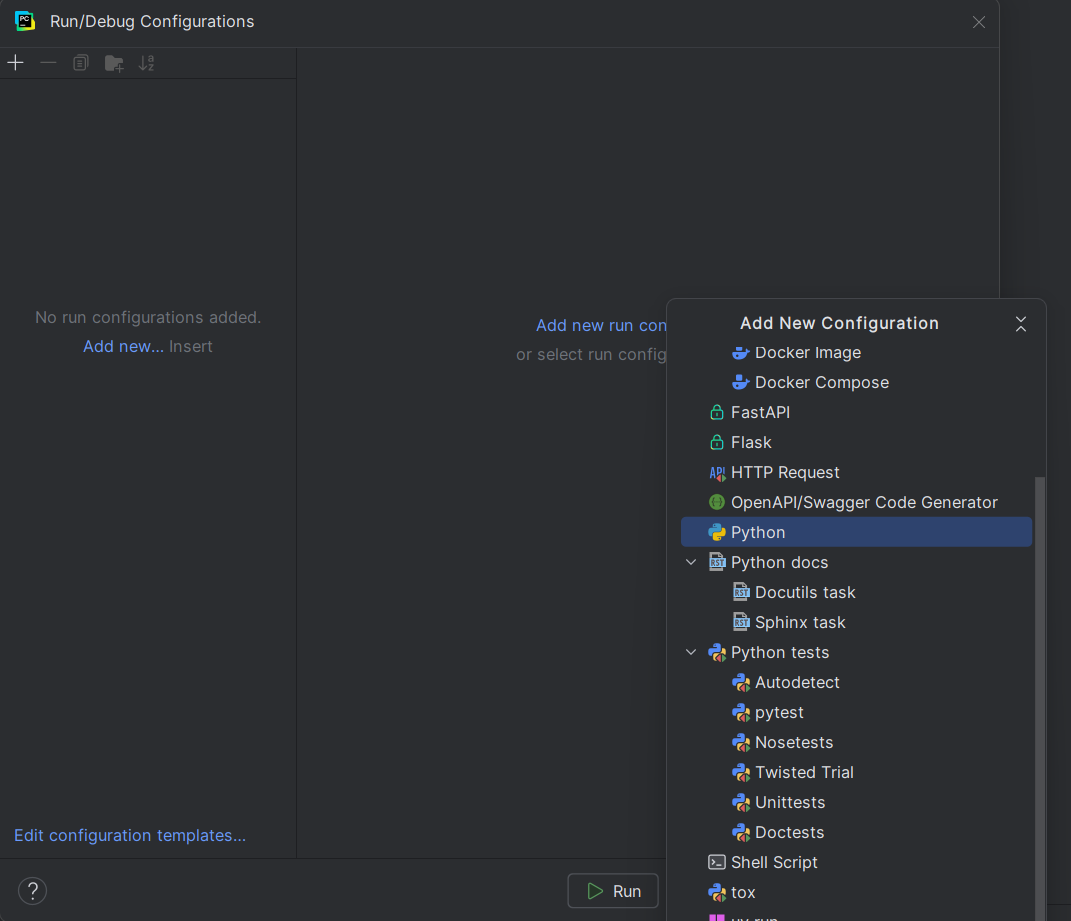
2. If creating a new configuration, select 'Python' from the list.
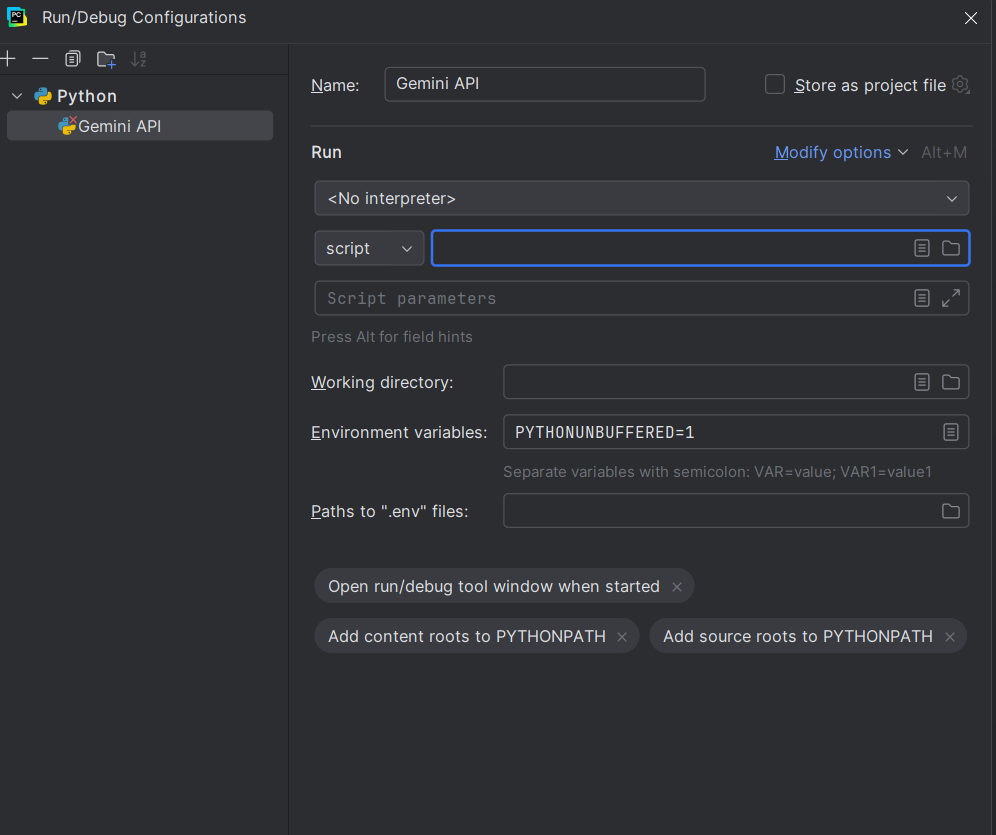
Step 5. Edit the Configuration
1. Name the configuration something appropriate, i.e., Gemini API.
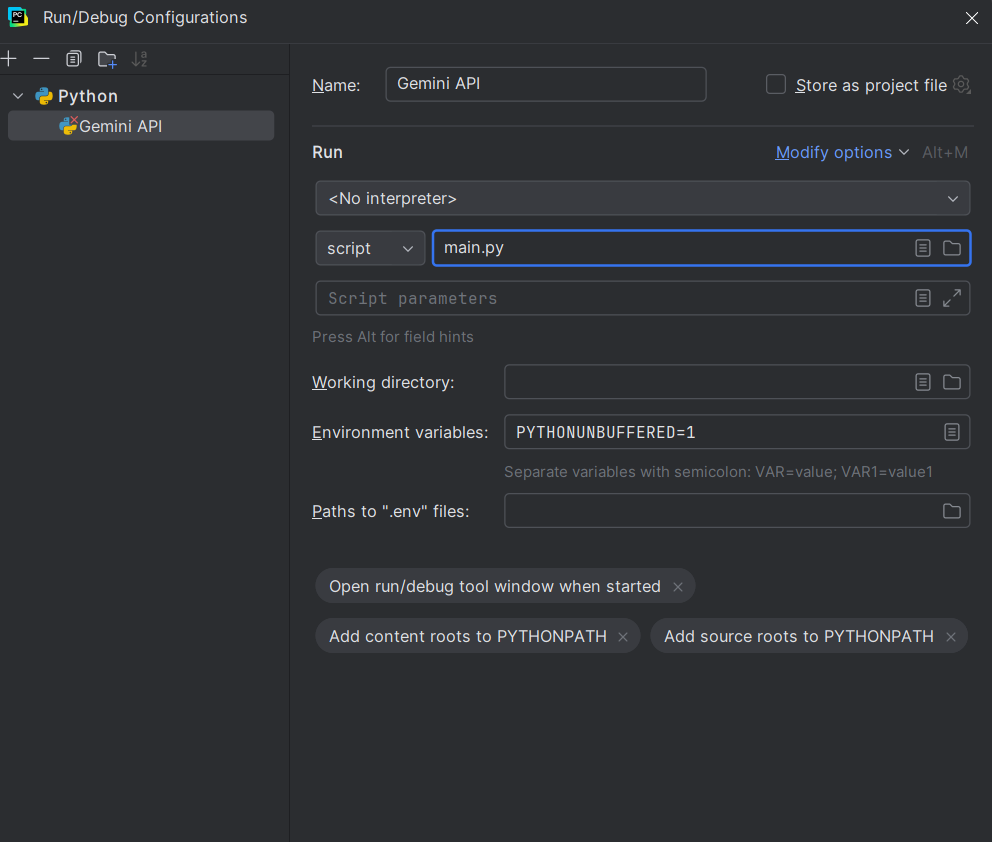
2. Under the 'Run' section, edit the 'Script' tab to your file (e.g., main.py)
3. In the 'Environment variables' field, click the 'Edit environment variables' button.
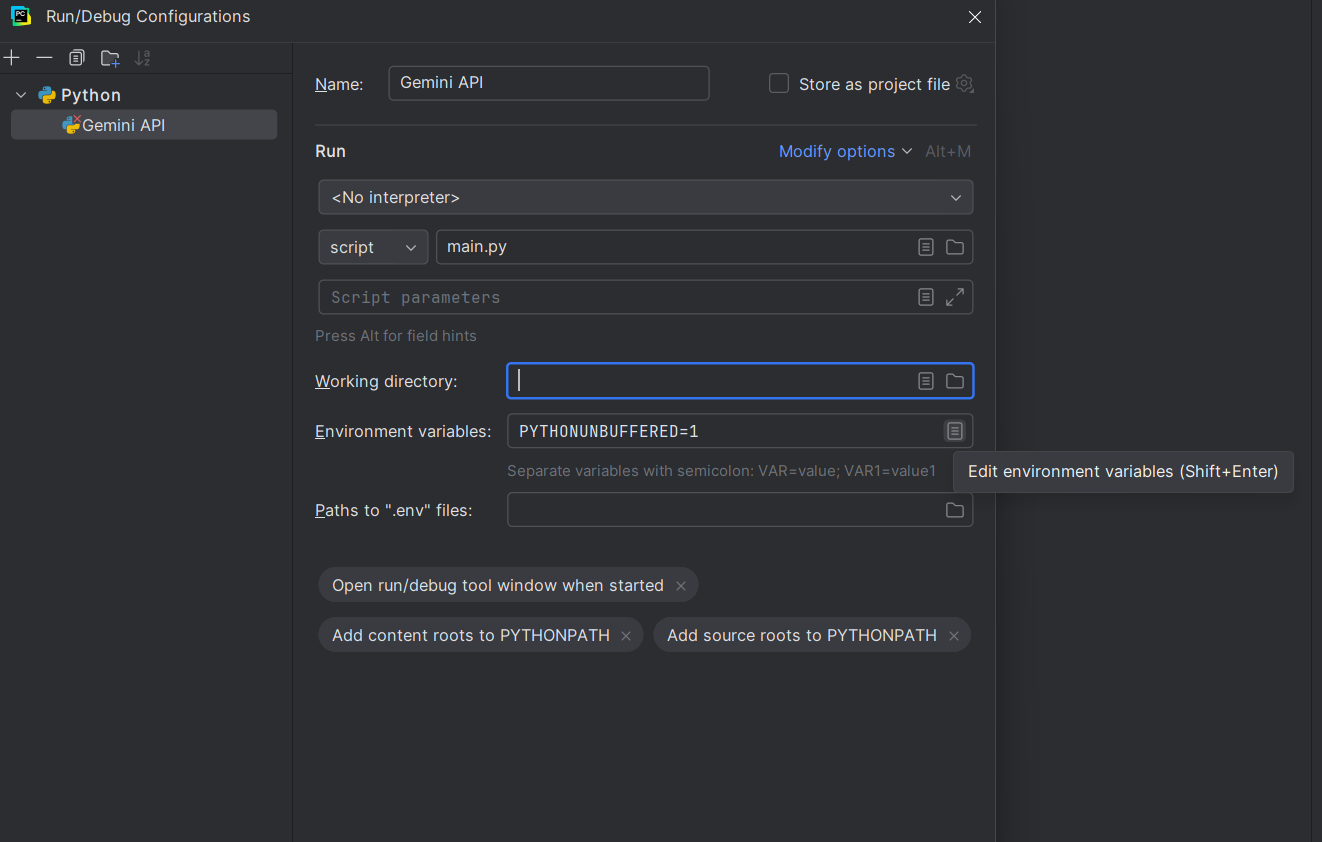
4. Click the 'Add' button.
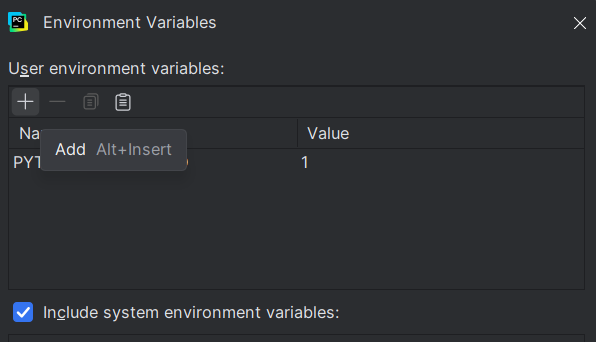
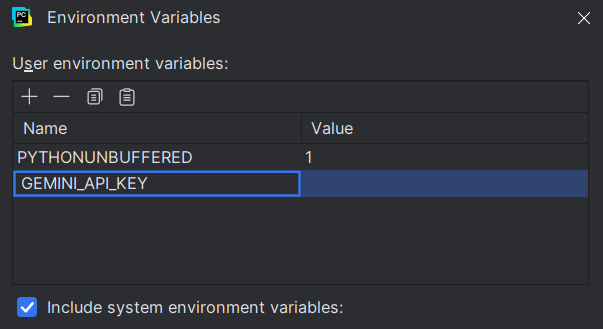
5. Name it something appropriate to the model, such as 'GEMINI_API_Key'.
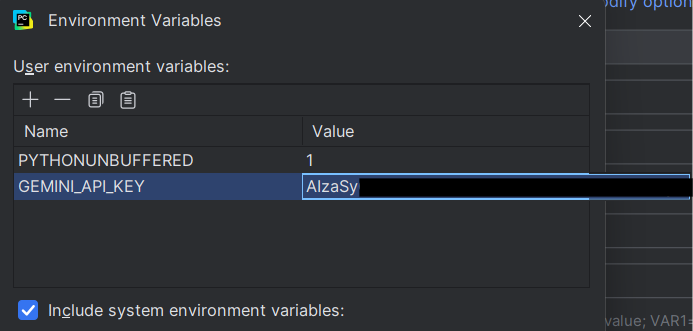
6. Under the 'Value' field, paste the API key you generated in Step 1.
7. Click 'OK' to save it.
8. At the end of the setup, your new configuration should look like this.
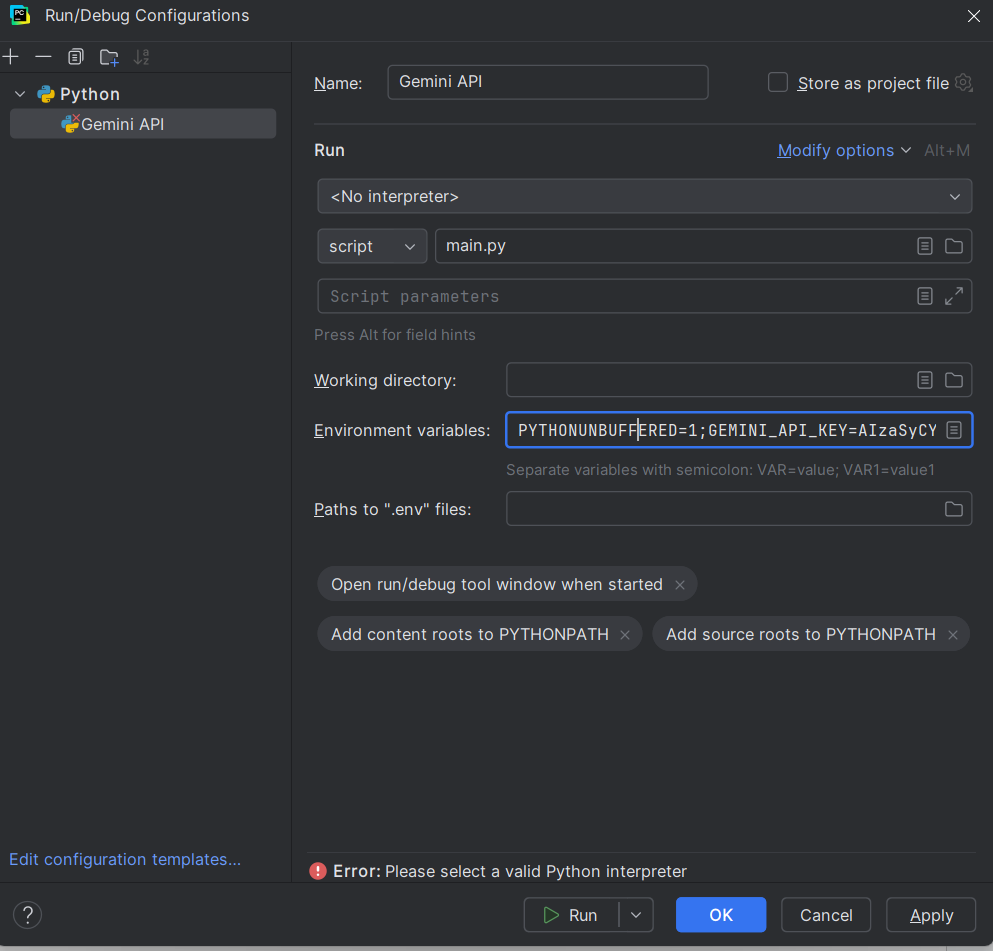
9. Click OK to complete the configuration.
Step 6. Run the API
Now, you'll have the LLM API directly linked to your project on PyCharm. You can select it by clicking the button at the top of the page.
However, do note that this doesn't turn PyCharm into an AI-powered editor, but instead keeps your API key securely available to any Python scripts run inside PyCharm.
It's best suited for advanced users building tools, experimenting with LLMs, or creating workflows that can call the API automatically without hardcoding credentials.
What Problems Can It Actually Solve?
There are multiple possible use cases for AI within PyCharm. Here are a few scenarios to consider:
Use Case 1: Code Generation
Scenario: For situations where you need multiple boilerplate routes, manually writing them can be a tedious and long process. Instead, you can use an AI plugin with a natural language prompt to ask it to help, such as:
This frees up time for you, while the AI provides you with a ready-made skeleton of code for you to refine logic to your needs. In essence, you tell the AI what you want, and it writes the code for you, which can be especially useful for repetitive, mundane tasks.
Use Case 2: Code Explanation & Debugging
Scenario: You've inherited a messy and complex script full of nested loops and cryptic variable names. This makes it confusing for you to understand what is what, giving you a tougher time working with the script.
In this situation, you could simply highlight a section of the script and ask the AI to describe what the function does with a prompt like:
The AI will break down the function in plain language, making it easier to spot flaws and understand the script.
Alternatively, if you've run into an error message, you can ask the AI a prompt after pasting the traceback:
The AI will then provide practical fixes you can try without having to manually look for a solution.
Use Case 3: Code Optimization & Refactoring
Scenario: After a strenuous and messy coding session, you've got a working function, but it's convoluted and hard to read. Select portions of your code you want to optimize and prompt the AI with something like:
Or
The AI will respond with a cleaner working version of the code, point out unnecessary steps, or suggest shortcuts.
The Key Takeaway
The scenarios mentioned above are real-world situations for programmers. But the common theme here is they all addressed these scenarios with actionable, real-world boosts to productivity.
This helps you save time, reduce stress and frustration with error messages, and lets you focus on solving real problems instead of repetitive, mundane tasks.
Conclusion
Integrating AI into PyCharm can be an effective way to streamline your coding workflow, offering features that boost productivity. While AI can help smooth the process, remember that true expertise and an in-depth understanding of how things work only come from hands-on practice, not from relying on AI alone.
LLMs in PyCharm help you write. GoInsight.AI helps you build. Orchestrate your AI-assisted code into end-to-end automated business processes.
Start Free Trial





Leave a Reply.