You've probably heard the term Generative AI, or Gen AI, and you might have been curious. But when you searched for it, you found pages full of dense jargon, complex professional terms, and topics that seemed only meant for industry insiders. So, you closed the tabs and moved on.
You're in luck. We understand that frustration. This article is designed specifically for curious beginners who have no technical background. We promise to skip the abstract principles, the complex data, and the long walls of text that make you want to quit reading.
Instead, we will use simple, conversational language to help you finally understand what Generative AI is.
What Is Generative AI in Simple Terms?
Let's start with the name. Generative AI (Gen AI) is a system designed to generate content. That means it can create brand-new output—like text, images, music, or code—in response to a simple prompt from you.
Unlike older forms of AI, Gen AI doesn't just analyze existing data; it uses that data to build something entirely original. It's the technology that powers popular tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney.
For example, when you ask ChatGPT to write a professional email, or use Midjourney to generate a unique image of a spaceship, these processes are inherently creative. They are taking your simple text prompt and generating a brand-new, original output that didn't exist a moment before.
What Is the Differences between Traditional AI & Generative AI?
To truly understand Gen AI, we need to compare it to the AI you've been using for years. In this context, we separate AI into two main families: Traditional AI and Generative AI.
Traditional AI
Traditional AI (or Discriminative AI) is the Judge. Its core task is to analyze, classify, and predict outcomes based on historical data. Simply put, it is to judge and choose the best answer from a known set of possibilities.
For examples:
- Spam Filter: It judges whether an email is spam or not-spam.
- Product Recommendations: It judges which item you are most likely to buy next.
- Facial Recognition: It classifies whether a face matches a database image.
Generative AI
Generative AI is the Creator. Its core task is to imagine and invent new material that didn't exist in its training data.Simply put, it is to create something novel based on the patterns it has learned.
For Examples:
- Writing an original blog post on a specific topic.
- Generating a photorealistic image of an unseen landscape.
- Writing a new section of code to solve a problem.
In one sentence, the difference is clear: Traditional AI helps you choose the best existing answer; Gen AI helps you create a brand-new answer.
Our View: This difference isn't just technical; it changes how we work.
In the past, we used AI primarily as an analyst to scrutinize data. Now, Gen AI has flipped the process. It handles the creative first draft—the most time-consuming part.
Your role changes from being a starter to being an editor or prompt engineer.
For example, an e-commerce employee agonizing over product descriptions can now simply give Gen AI a prompt, generate many options instantly, and then only focus on selecting and optimizing the best one. The work shifts from zero-to-one creation to review and refinement.
How Generative AI Learns and Creates
If Gen AI is not a traditional computer program, how does it actually 'create' content? The secret is surprisingly simple: statistics and prediction.
Think of Gen AI as the World's Best Guessing Machine or the Most Logical Statistician.
The Core Mechanism: (Next-Word) Prediction
The entire process boils down to Prediction. The AI doesn't understand language like a human; it understands statistical relationships.
It has been trained on a massive amount of data (often the entire public internet, or terabytes of human language).
When you start a sentence, the AI calculates the highest probability of the next word appearing in that context. It then locks that word in and repeats the process, token by token, until the article is complete.
For example, if you start a query with "The cat sat on the...", the AI calculates that "mat" or "rug" have a much higher probability than "moon" or "bicycle." It chooses the most likely word ('mat'), and then predicts the next word based on the new, completed phrase.

The Engine: The Transformer Architecture
Why is modern Gen AI so much better at guessing than the old autocomplete on your phone? The difference is the engine: the Transformer architecture.
This technology allows the AI to efficiently understand long-distance context. It remembers the beginning of a conversation, not just the last few words.
This ability to grasp long-range dependencies is what makes the output coherent, logical, and flowing, rather than just a series of random guesses.
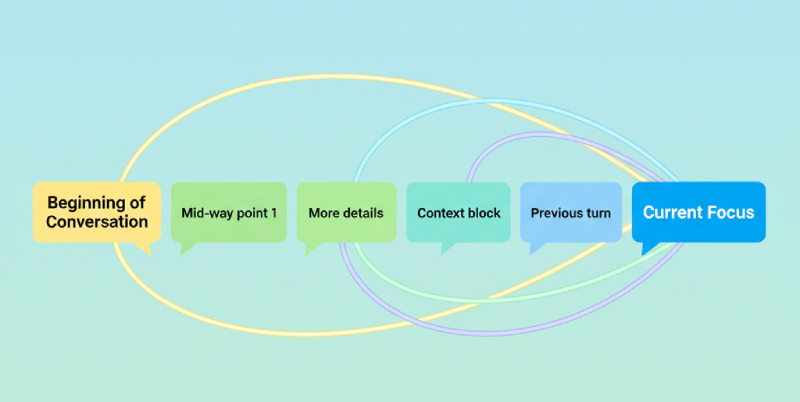
For example, a simpler AI might forget a specific instruction after a few sentences. However, a Transformer-based Gen AI can be asked to write a letter in the specific style of a 19th-century author and keep that archaic, consistent tone for ten paragraphs, maintaining the long-range dependency on that specific 'style' throughout the entire content.
Our View: The sheer scale of the data and the model size is what makes Gen AI powerful.
It has absorbed the patterns of human language to an extreme degree. Its answers are smooth and logical, not because it has human-like understanding, but because it has perfectly simulated the statistical patterns of language.
However, this also leads to a thought: Is it truly understanding what you are saying, or is it just perfectly simulating the statistical patterns of a human speaking?
5 Real-World Applications of Gen AI
Gen AI is rapidly changing virtually every field. Here are six core areas where you can see its value immediately:
- Content Creation: Draft emails, blog outlines, scripts, meeting summaries, etc. This helps eliminate the dreaded "blank page" problem and drastically cuts down the time spent on routine communication.
- Art & Design: Generate unique images, logos, or design prototypes just from a text description. This democratizes design, and anyone can visualize complex ideas instantly, saving hours of manual labor or expensive fees.
- Software Development: Auto-complete lines of code, translate code snippets between different programming languages, or help debug errors. It frees up engineers to focus on high-level architecture and problem-solving, rather than repetitive coding tasks.
- Synthetic Data: Create realistic, fake datasets for training other AI models. The advantage is privacy and quality; it helps protect real user privacy while ensuring AI models are trained on high-quality, representative data.
- Customer Experience and Business Optimization: Power smart customer service agents and provide an internal knowledge search. The payoff is instant service; it provides 24/7 instant, natural support, significantly reducing call center load and improving customer satisfaction across large businesses.
Gen AI Also Has Limits
No powerful tool is without flaws. Now that you've seen how GenAI can explore every aspect of our lives, you should also be aware of its limitations.
Hallucination
If you've ever asked Gen AI for a list of reference books or a set of citations for your paper, you might have experienced this:
AI provides wrong information, invents sources or citations, or mixes real facts with fiction, all while sounding perfectly authoritative. Even if you correct it, it might generate a new correction that is still entirely fabricated under the guise of "fixing" its mistake. This is called Hallucination.
But you need to understand: the hallucination is an inherent statistical feature, not a bug. AI doesn't access a facts database; it only predicts the statistically most coherent sequence of words. When its confidence is low, it compensates by creating a sentence that sounds like the truth.
Simply put, AI prioritizes coherence over truth. This is why you should always verify critical information generated by Gen AI.
Bias
Gen AI models are trained on real-world data, and that data reflects real-world human biases (social, racial, and gender). The AI might inherit and even amplify these biases, leading to unfair or skewed outputs.
For example, if you ask the AI to generate images of "successful CEOs," it might predominantly show white men simply because that was the majority representation in its training data. This makes the output incomplete and often unfair.
So, when using Gen AI, you must be the final check for fairness. If you spot bias in the output—whether in an image or a piece of text—your job is to adjust your prompt to be more inclusive and specific, or discard the biased result entirely.
Timeliness
Many popular models (especially free or older versions) have a knowledge cut-off date. They were trained up to a certain point in time, meaning they cannot give you information about current events or recent developments.
So, if you need recent or time-sensitive information, we strongly recommend you enable Deep Research or Web Search features within your Gen AI tool. This is currently the primary way to alleviate the Timeliness limitation by allowing the AI to search the real-time internet.
Conclusion
You now understand the fundamental difference: Gen AI is the Creator, shifting your work from creation to editing.
We encourage you to use Gen AI to explore its possibilities, but remember to view it as a powerful tool that makes work more efficient, allowing you to focus on judgment and strategy, not a replacement for your intellect.
GoInsight.AI's GoInsight Workspace is an enterprise-grade AI portal that unifies your company's existing AI tools and workflows into a single conversational interface, benefiting everyone.
Start Free Trial





Leave a Reply.