- What Is an AI Agent? A Simple Definition
- How AI Agents Work: The Engine Inside
- Best Real-World AI Agent Examples
- 1. Customer Support & Helpdesk Agent
- 2. Internal HR Assistant (Onboarding Agent)
- 3. IoT Status & Incident Response Agent
- 4. Finance & Invoice Processing Agent
- Getting Started: Building Your First AI Agent with GoInsight.AI
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving rapidly, and we're seeing that evolution in the shift from chatbots—essentially reactive AI tools—to proactive AI Agents capable of planning, decision-making, and autonomous action. Think about the difference between a chatbot that just gives you an answer and an AI Agent that can set tasks in motion.
Multiple AI Agents will collaborate, each specializing in a particular domain. For instance, one agent might handle data gathering, another interprets that data, while yet another focuses on visualization.
By the end of this article, you'll:
- Understand the basics of AI Agents and why they're more than just chatbots.
- Discover the key components in an AI Agent's architecture, from planning to memory.
- Know four powerful AI Agent examples and their best pratices.
- Learn how to start building or integrating AI Agents in GoInsight.AI.
1. What Is an AI Agent? A Simple Definition

Understanding the AI Agent: More Than Just a Chatbot
An AI Agent is best thought of as a specialized digital employee. Whereas chatbots respond to your questions, AI Agents can be instructed to fulfill a goal, carrying out a series of steps with minimal human oversight. This includes absorbing context, evaluating potential strategies, executing tasks, and iterating to refine or correct its approach.
Simple Analogy: Imagine you hand over a multi-step assignment to a reliable colleague. You say, "Please update our client database, compile a report on recent sales, and send me the final document by Monday." That colleague coordinates these actions, checks for errors, and notifies you only when needed. An AI Agent aims to replicate this type of proactive behavior digitally.
Core Characteristics (The S.P.A. Model)
- 1.Sense
The agent perceives its environment, whether that environment is user input, third-party APIs, software logs, or files in a local directory. It "listens" to or "reads" data, gathering the information it needs to carry out tasks. - 2.Plan
After it gathers relevant input, the agent develops a strategy. Using a reasoning framework or an internal "mental model," it breaks down the goal into smaller tasks and decides which steps to take. - 3.Act
With the plan in place, the agent carries out each step by calling tools, writing code, sending emails, or performing whatever task is required. Once it acts, it can observe the results, refine its plan, and repeat the process.
Key Differentiator: Traditional models (like a chatbot) passively wait for queries and respond. In contrast, an AI Agent is goal-oriented and capable of making decisions with minimal prompting. This autonomy empowers it to handle more complex tasks that span multiple steps—an important consideration in real-world settings where end-to-end automation is essential.
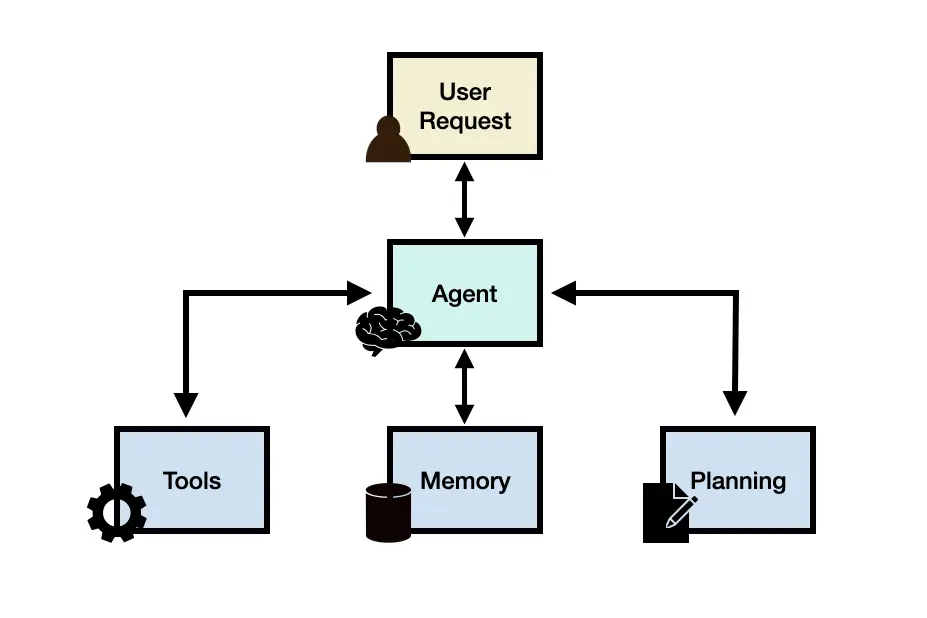
2. How AI Agents Work: The Engine Inside
The Architecture of an AI Agent: Planning, Memory, and Tools
Despite the complexity of what AI Agents can do, the basic architecture is fairly straightforward. A helpful way to visualize it is:
Sense -> Plan -> Act -> Observe -> Repeat
This cycle continues until the agent achieves its goal or runs into a limitation (e.g., insufficient data or user permission).
Core Components Explained
- 1.Planning Module
Often referred to as the agent's "brain," this component figures out a path from the initial request to the final result. It can involve advanced logic like ReAct (short for Reason + Act), where the agent reasons about each step before acting. This module is vital for multi-step tasks that require adapting to new information or unforeseen obstacles. - 2.Memory Module
Agents need to recall their previous actions and decisions so they can keep improving. - Short-Term Memory: Useful for the immediate task, storing context about what the agent is currently doing.
- Long-Term Memory: Retains ongoing insights about user preferences or specialized knowledge that guides future actions.
- 3.Tool Use Module
Think of tools as the "hands" or "instruments" the agent uses to interact with its environment. Examples include a code compiler, a web browser, a database query tool, or a text-generation function. The agent decides which tool to use and how, enabling it to read from or write to external systems.
3. Best Real-World AI Agent Examples
Below are four real-world AI agent examples that can be realized using GoInsight.ai. Each example highlights how GoInsight.ai's workflow orchestration, multi-agent support, and built-in AI capabilities empower you to deploy robust, enterprise-grade AI agents. We've also included best practices to help ensure long-term success.
Customer Support & Helpdesk Agent
Overview
Provides 24/7 automated responses to customer inquiries, retrieves relevant FAQs or knowledge-base articles, logs escalations, and hands off complex cases to human support.
How GoInsight Implements It:
- Interactive Flow Bot: Build an AI-powered chatbot flow that integrates with your CRM or ticketing system via HTTP Request nodes.
- Knowledge Base (RAG): Use GoInsight.ai's knowledge-base retrieval nodes to surface internal help articles or documentation.
- LLM Nodes: Fine-tune responses or summarize multi-paragraph user requests.
Best Practices:
- Human-in-the-Loop: Set a threshold for confidence or escalation so the bot automatically transfers complicated tickets to live agents.
- Token/Cost Monitoring: If the agent handles large volumes of queries, set usage limits or alerts to prevent unexpectedly high LLM costs.
- Continuous Training & Feedback: Analyze logs to identify where the agent struggled or gave incomplete answers. Update FAQ entries and prompts accordingly.
Internal HR Assistant (Onboarding Agent)
Overview
Guides new hires (or existing employees) through onboarding steps—forms completion, policy acknowledgments, training schedules, etc. Answers HR-related queries, like "What is our vacation policy?" or "How do I request maternity leave?"
How GoInsight Implements It:
- Service Flow Bot: Let employees ask HR questions via Slack or Teams, automatically routing the query to the HR knowledge base or relevant policy.
- Dynamic Forms & Approvals: Use interactive prompts to capture employee info, store data in HRIS, and send emails or notifications for approvals.
- Document Generation: Text Template node can generate PDFs or HR documents (e.g., an offer letter or NDA).
Best Practices:
- Department Isolation: Use GoInsight's role-based access controls so HR data remains private to authorized members.
- Up-to-Date Knowledge: Keep the HR knowledge base current by adding new company policies and automating the re-indexing.
- Multi-Channel Integration: If employees use a company portal or chat tools, embed the HR Assistant directly there for ease of access.
IoT Status & Incident Response Agent
Overview
Monitors IoT devices in manufacturing plants, warehouses, or retail chains.
Uses AI to interpret device error logs or sensor data, automatically opening an incident if anomalies arise (e.g., temperature spike, device offline).
How GoInsight Implements It:
- Scheduled or Event-Triggered Service Flow: Poll IoT endpoints or receive webhook alerts, parse sensor data with JSON nodes, apply gating logic.
- Anomaly Detection: Use Python code nodes or LLM nodes to interpret unusual logs or event text.
- Automated Notifications: If a device anomaly meets certain thresholds, the flow sends alerts to Slack/email or triggers a field technician request.
Best Practices:
- Edge vs. Cloud: Decide which data is processed locally vs. in GoInsight.ai, especially if you have bandwidth or latency concerns.
- Threshold Calibrations: Set appropriate tolerance levels for "normal" vs. "abnormal" device readings.
- Redundancy & Fallback: Ensure you handle connection issues gracefully—especially critical in industrial IoT settings.
Finance & Invoice Processing Agent
Overview
Automatically extracts invoice data (vendor, amount, due date) from PDF or email attachments, validates entries, and initiates payments or approval flows in ERP systems.
How GoInsight Implements It:
- Document Parsing: Combine a file-upload interactive step with an LLM or OCR (optical character recognition) integration to read invoice details.
- ERP Integration: With HTTP Request nodes, post validated invoice records to SAP, Oracle, NetSuite, or other finance systems.
- Automated Approvals: Use Condition nodes to check if an invoice meets your predefined business rules (e.g., if over $10,000, route to CFO for sign-off).
Best Practices:
- Secondary Verification: For high-value invoices, use a second AI agent or a human reviewer to confirm extracted data matches the PDF.
- Data Privacy: Keep sensitive payment info restricted to specific roles or subflows with limited access.
- Audit Trail: Leverage GoInsight's built-in logging so each invoice node execution is traceable for compliance purposes.
4. Getting Started: Building or Integrating Your First AI Agent
How to Leverage AI Agents: A Practical Guide for Decision-Makers and Developers
For CTOs, PMs, and developers, one of the biggest questions is how to introduce AI Agents into your current tech stack. There are generally three routes: build your own from scratch, buy a turnkey solution, or integrate a blend of open-source and commercial services.
The Strategic Choice: Build vs. Buy vs. Integrate
Below is a quick comparison table that highlights cost, customization, time-to-market, and required expertise:
| Approach | Description | Cost | Customization | Time-to-Market | Expertise Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Build | Create an agent in-house using open-source frameworks and your own infrastructure. | Potentially high (software + hardware) | High | Longer | High |
| Buy | Purchase a commercial agent solution (e.g., managed AI platform). | Subscription fees (possibly usage-based) | Low–Medium | Faster | Low–Medium |
| Integrate | Combine open-source components with existing proprietary tools. | Moderate | Medium–High | Moderate | Medium |
- Build: Ideal if you need full control and can handle the engineering overhead.
- Buy: Great for smaller teams seeking rapid deployment or a "hands-off" approach.
- Integrate: Offers a balance if you have some developer resources but also want simplicity.
GoInsight.AI- Best Frameworks and Platforms for Building AI Agents
GoInsight.ai – the AI platform designed to unleash the power of AI Agents in your business. With GoInsight.ai, creating powerful AI agents is easier than ever. It provides a low-code platform where businesses can create and deploy custom AI agents tailored to specific workflows.
The platform leverages multiple LLMs to optimize performance, while continuously monitoring and refining agent behavior through built-in analytics and feedback loops. So, whether you need agents for customer support, sales, research, or workflow automation, this platform DOES IT ALL.
GoInsight.ai stands out:
- Visual Workflow Builder
- Multi-Agent Collaboration
- Built-In AI and Knowledge Base
- Simple Monitoring & Control
- Fast to Deploy, Easy to Scale
Conclusion
Whether you're new to this technology or looking to expand your existing AI strategy, AI Agents represent a major leap forward. They move beyond simply returning responses to actively planning and doing the sort of multi-step tasks that previously required teams of people or a sprawling set of separate automation tools.
By leveraging GoInsight.ai's multi-agent system, visual flow builder, and built-in enterprise features, you can rapidly deploy these AI agent scenarios—and many more—while maintaining robust control over security, reliability, and lifecycle management.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What is the main difference between an AI Agent and a chatbot?
A: A chatbot primarily reacts to user input within a conversation. An AI Agent is proactive and goal-oriented; it can create and execute a multi-step plan using various tools (like browsing the web or writing code) to achieve a goal, often without step-by-step human guidance.
Q: How much does it cost to run an AI Agent?
A: Costs can vary dramatically. It depends on the complexity of the task, the LLM used (e.g., GPT-4 is more expensive than GPT-3.5), and the number of "steps" or tool uses the agent performs. A simple task might cost pennies, while a complex research task could cost several dollars.
Q: Can AI Agents learn and improve over time?
A: Yes. Agents can be designed with memory systems that allow them to learn from past interactions, successes, and failures. This can involve storing feedback in a vector database to refine future plans and actions, making them more effective over time.






Leave a Reply.