Understanding AI Agents: How They Work and Why They Matter
Beyond basic chatbots, AI agents represent a new way of interacting with software—they can think, plan, and act independently. Unlike traditional automation tools that follow static rules, these agents adapt to changing conditions and carry out complex tasks with minimal human input.
As both individuals and businesses look for smarter ways to handle repetitive work, this guide will break down what AI agents are, how they work, and where they’re making a real impact.
What Are AI Agents?

An AI agent is an autonomous software system that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant human supervision. You can think of it as a digital employee powered by large language models (LLMs), capable of reasoning and interacting with tools and platforms.
What sets AI agents apart from traditional bots is their autonomy and adaptability. While a conventional chatbot follows fixed rules and responds to predefined inputs, an AI agent can understand complex situations, plan several steps ahead, and adjust its behavior as conditions change.
For example, a basic customer support bot can only respond to pre-programmed questions. An AI agent, on the other hand, can interpret nuanced customer requests, retrieve information from different systems, and even escalate issues intelligently when needed.
How AI Agents Work?
AI agents operate through a continuous loop of perception, reasoning, and action. This decision-making cycle allows them to work autonomously while staying aligned with their goals.
The Three-Phase Process
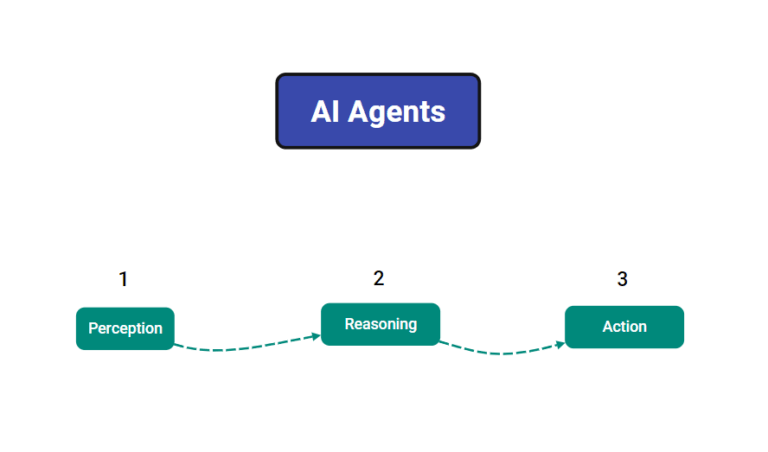
● Perception: The agent first gathers information from its environment. This might include reading emails, analyzing data streams, monitoring alerts, or collecting user input. It processes this information to understand the current context and set priorities.
● Reasoning: In this phase, the agent evaluates the data and develops a strategy. It weighs different options, predicts outcomes, and decides on the best course of action—often using large language models and decision frameworks. This ability to plan and adapt is what sets AI agents apart from basic automation.
● Action: The agent then executes its plan by interacting with tools, APIs, or systems. This could involve updating records, triggering workflows, sending notifications, or performing other tasks across platforms.
Imagine an AI agent that manages incoming emails. It reads the message, identifies the sender and content (perception), determines its priority and category (reasoning), then takes action—filing it, sending a response, or forwarding it to a colleague.
Unlike traditional email rules, this agent continuously adapts based on context and learns from outcomes, making it more intelligent and reliable over time.
Key Components of an AI Agent
AI agents are built from several key components that work together to support autonomous behavior. Understanding these parts helps explain why AI agents are so flexible, responsive, and intelligent.
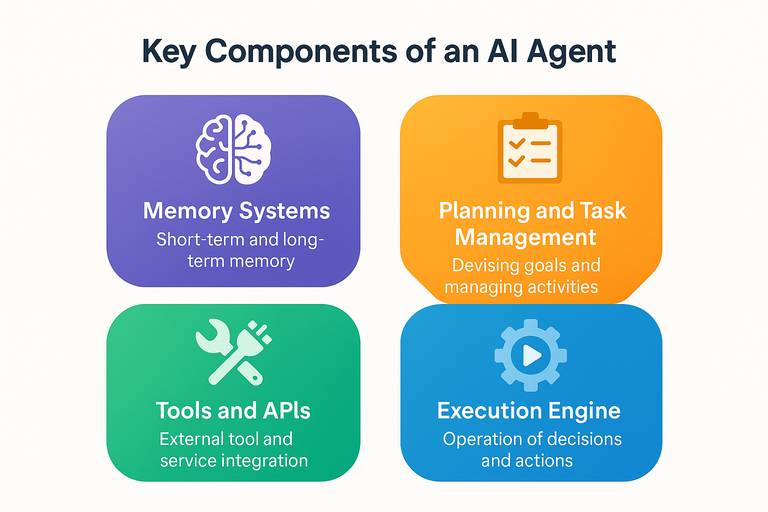
Memory Systems
Memory allows agents to retain context and learn over time. Short-term memory helps maintain conversation context or task state, while long-term memory stores past interactions, user preferences, and learned patterns. This dual-memory structure enables more personalized and consistent behavior.
Planning and Task Management
This component lets agents break down complex goals into smaller, manageable steps. It handles prioritization, resource coordination, and scheduling. More advanced agents can even adapt their plans when new information arrives or obstacles appear mid-process.
Tools and APIs
Think of tools and APIs as the agent’s hands and eyes—they allow it to interact with the outside world. By accessing external systems, databases, and services through APIs, the agent can complete tasks far beyond its built-in capabilities.
Execution Engine
The execution engine is the operational core of the agent. It ensures that decisions are carried out reliably, manages errors, and maintains system stability throughout the task lifecycle. Without this component, even the best reasoning would never translate into action.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be categorized in different ways depending on their capabilities, purpose, and complexity. Below are three common classification approaches:
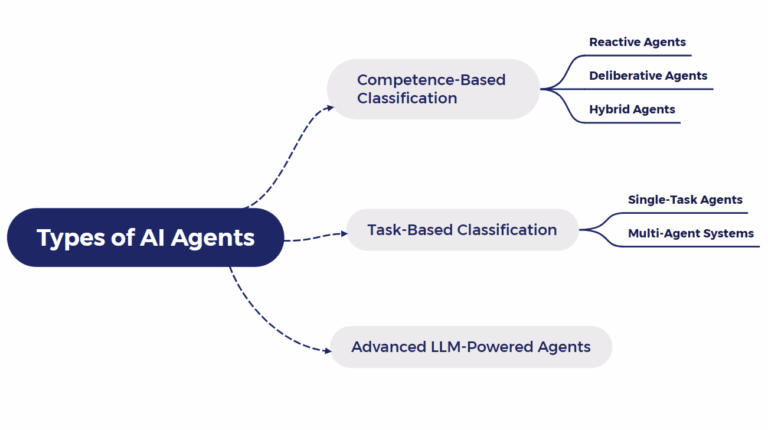
Competence-Based Classification
Reactive Agents respond immediately to changes in their environment without deep analysis or planning. They’re well-suited for simple, real-time applications such as basic customer support or sensor-based monitoring.
Deliberative Agents process information, plan ahead, and make calculated decisions. These agents are ideal for complex problem-solving tasks that require foresight and reasoning.
Hybrid Agents combine both reactive and deliberative approaches. They can quickly respond to urgent events while also planning more deeply when time and context allow.
Task-Based Classification
Single-Task Agents are designed for a specific function like summarizing emails, generating content, or sorting data. Their focused nature allows for high efficiency within their domain.
Multi-Agent Systems involve multiple agents working together—each specialized in a particular task. These collaborative systems can tackle complex goals that a single agent would struggle to handle alone.
LLM-Powered Agents
At the forefront of AI development are large language model (LLM)-powered agents, such as AutoGPT or BabyAGI. These agents combine reasoning, memory, and tool usage to autonomously complete open-ended tasks. With minimal programming, they can adapt to new challenges, generate creative ideas, and even coordinate workflows across multiple tools and platforms.
Real-World AI Agent Examples

AI agents are already embedded in many real-world applications across industries, helping organizations automate tasks, improve efficiency, and deliver smarter user experiences. Here are a few key examples:
Customer Service Agents
Modern AI agents go beyond traditional chatbots. They can access customer records, search internal documentation, and resolve complex inquiries—sometimes even triggering backend workflows. Platforms like Zendesk and Intercom now integrate AI agents that handle ticket routing, generate personalized responses, and escalate high-priority issues to human agents when needed.
Development Assistants
Tools like GitHub Copilot and other AI coding companions are transforming software development. These agents suggest code, debug errors, understand project contexts, and offer architectural guidance—allowing developers to focus more on design thinking and complex logic.
Workflow Automation Agents
Automation platforms like GoInsight.AI, Zapier and n8n leverage AI agents to orchestrate cross-platform workflows. These agents monitor triggers, apply business rules, and execute multi-step processes across apps—such as syncing CRM data, sending emails, or updating spreadsheets—all without manual input.
Research & Analysis Agents
AI-powered research assistants can gather, summarize, and analyze information from multiple sources. Whether it’s tracking market trends, compiling competitive intelligence, or generating internal reports, these agents help users save time and avoid information overload.
Sales & Marketing Agents
These agents support lead qualification, personalize outreach messages, schedule follow-ups, and sometimes even handle basic contract negotiations. By automating repetitive tasks, they allow sales and marketing teams to focus more on relationship-building and strategy.
Building Enterprise-Ready AI Agents with GoInsight.AI
Understanding AI agents is one thing—building them is another. Most traditional tools only offer limited automation or simple chat interfaces. But real agentic systems require orchestration, reasoning, tool use, and collaboration.
GoInsight.AI bridges that gap. It’s a visual, low-code AI automation platform designed specifically for building robust, enterprise-grade AI agents. Whether you're prototyping a single agent or designing a multi-agent system, GoInsight provides the power and flexibility to go from idea to implementation.
Key features:
- Visual AI workflow builder with drag-and-drop logic, model calls, and external APIs
- Multi-agent system support to coordinate tasks across specialized agents
- Integrated RAG and knowledge base support for contextual, memory-driven responses
- Human-in-the-loop collaboration, letting you define when agents need human review
- Enterprise-grade governance, including RBAC, audit logs, and on-premise deployment
If you're ready to move beyond theory and start building real agents, GoInsight.AI is a powerful platform to bring your vision to life.
Conclusion
AI agents are poised to become increasingly sophisticated, capable of handling more complex tasks and integrating seamlessly into both personal and professional workflows. The examples explored in this article are just the beginning of what’s possible when artificial intelligence is applied to real-world scenarios.
Whether you're an individual looking to automate repetitive tasks or a business aiming to streamline operations, exploring AI agents can help unlock new levels of productivity, creativity, and efficiency.






Leave a Reply.