- What Are AI Agent Frameworks?
- Key Components of AI Agent Frameworks
- 5 Developer-Centric Frameworks - If You Have a Technical Team
- 2 Collaborative & Low-Code Platforms: If You Don't Have a Technical Team
- 1 Conceptual Frameworks: If You Just Want to Experiment
- How to Choose the Right AI Agent Framework
- Best Practices & Tips
- Bonus: Get Started with AI Workflow on GoInsight.ai
AI agents can automate a huge range of tasks, but without a proper system, building them can be a messy process.
This is where AI agent frameworks come in. Think of them as a simple starter kit that helps you build powerful AI systems and get your work done faster.
This guide will help you understand what they are and how to choose the right one to get your work done faster.

What Are AI Agent Frameworks?
At their core, AI agent frameworks are a "starter kit" for building intelligent, autonomous systems. They come with prebuilt modules for essential capabilities like memory, reasoning, and tool integration.
Think of it this way: instead of building every component from scratch, these frameworks give you a foundation to get started immediately. They allow your AI to:
- Chain together different modules to complete tasks.
- Integrate with external tools and APIs.
- Manage knowledge and remember past conversations.
- Collaborate with users or other AI agents.
These frameworks reduce the complexity of deploying AI agent systems and accelerate the entire building, deployment, and management process.
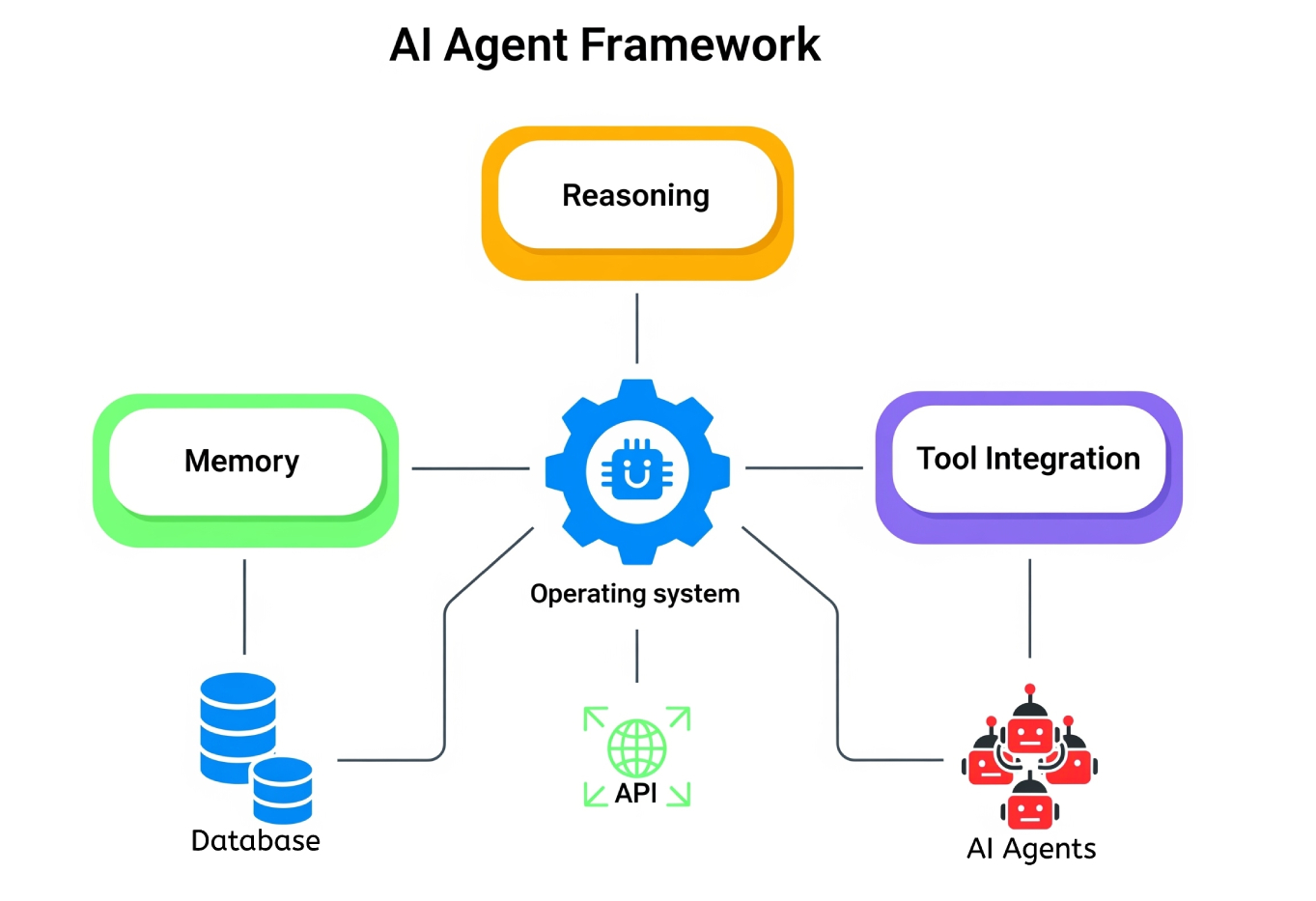
Key Components of AI Agent Frameworks
AI agent frameworks are built from a few essential components. While this isn't an exhaustive list, here are some of the most integral parts that make autonomous AI systems possible:
| Component | What It Is | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Agent architecture | The 'core' of your AI agent that determines how it plans, reasons, memorizes, and acts based on its training | Makes your agent 'smart' and function autonomously for its given tasks |
| External interfaces/tool integration | Connections to external tools via APIs, databases, or other software | Allows agents to connect to external platforms to fetch data, control systems, or use tools to perform tasks |
| Task management | Defines, assigns, and tracks tasks for deployed AI agents | Allows multi-step workflows and multi-agent coordination within systems |
| Communication protocols | Facilitates agent-to-agent or agent-to-user interactions | Makes teamwork between agents and communication with users (customers/employees) possible |
| Reasoning & planning | Required logic to allow agents to make decisions, 'think', and determine how they react to situations & environment | Empowers agents to intelligently approach problems and figure out action steps |
| Memory/state persistence | A stored database of info, context, and past interactions/outcomes | Allows agents to stay consistent over time, learning from past interactions, and 'remembering' conversations with users |
| Monitoring & debugging | Dashboards, logs, and tracing tools are used to track, inspect, and adjust agent behavior | Allows teams to spot errors & agent efficiency to improve performance and ensure reliability |
How to Choose an AI Agent Framework?
Choosing the right AI agent framework can feel complex, but it doesn't have to be. This guide simplifies the process for business leaders and non-technical users.
We've organized the top frameworks around one simple question: Do you have a technical team?
Your answer places you into one of three categories:
Find your section below, and let's match you with the perfect tool.
Developer-Centric Frameworks - If You Have a Technical Team
These frameworks offer maximum power and flexibility. They are the best choice if you have professional developers ready to build a custom, deeply integrated AI solution.
1LangChain
Think of LangChain as the ultimate LEGO set for building AI applications. It provides a vast collection of modular components that your developers can assemble in countless ways to create highly customized solutions that connect to any data source or tool.
Selling Points
Unmatched Flexibility: Offers near-limitless possibilities for custom application logic.
Largest Ecosystem: Supported by the largest community, with the most integrations and examples available.
Comprehensive Tooling: Provides a complete toolkit covering everything from data connection to agent orchestration.
Choose it when:
- Your team wants to build a highly customized AI application from scratch.
- Your workflow needs to integrate a wide variety of data sources or APIs.
- You want a mature framework with extensive community support.
Don't choose it when:
- Your team has no developers, or you want to avoid any code development.
2LangGraph
Where LangChain offers a box of parts, LangGraph provides the blueprint. It's an extension of LangChain designed for building highly reliable, step-by-step agents. It allows developers to define a process as a clear flowchart, ensuring the agent's behavior is predictable, controllable, and easy to debug.
Selling Points:
Precise Process Control: Enables you to build agents that follow a strict, flowchart-like logic, perfect for business processes.
High Reliability for Complex Tasks: Its structure makes it more stable and less prone to errors in multi-step workflows.
Built-in Human-in-the-Loop: Easily add steps that require a person's approval before the agent continues.
Choose it when:
- You need to build a task that involves complex decision logic or requires multiple iterations to complete.
- Your business demands a high degree of stability and reliability from its AI agents.
Don't choose it when:
Your workflow is a simple, linear task that doesn't require complex control.
3Microsoft AutoGen
AutoGen enables you to create a team of specialized AI agents that "talk" to each other to solve problems. You define the roles (e.g., "Planner," "Coder," "Tester"), and they autonomously collaborate through conversation to complete a complex task.
Selling Points:
Conversational Agent Collaboration: Its unique strength is enabling agents to solve problems through automated conversation and debate.
Automated Task Decomposition: Excellent for complex, open-ended problems where the solution path isn't clear from the start.
Multi-Role Specialization: Allows you to build a virtual team where each AI has a specific expertise, mimicking a real-world expert group.
Choose it when:
- Your business requires multiple AI agent roles to work together (e.g., a researcher, a writer, and an editor).
- You want to build a system that can automatically break down and assign a problem to different agents.
Don't choose it when:
You only need a simple, single-agent task.
4OpenAI Agents SDK
For teams already building with OpenAI models, this SDK is the official, streamlined toolkit for creating agents. It's a lightweight library focused on making it simple for agents to pass tasks between one another, perfect for quick development and iteration within the OpenAI ecosystem.
Selling Points:
Official OpenAI Toolkit: Ensures seamless integration and compatibility with the latest OpenAI models and features.
Lightweight and Fast: Designed for simplicity and speed, avoiding unnecessary complexity for core tasks.
Ecosystem Native: The most natural choice for developers already heavily invested in OpenAI's platform.
Choose it when:
- Your development team is already heavily invested in the OpenAI ecosystem.
- You need a simple, fast-to-implement solution for multi-agent hand-offs.
Don't choose it when:
You need to integrate with a non-OpenAI model or a vast, complex external ecosystem.
5Semantic Kernel
Semantic Kernel is Microsoft's answer to building enterprise-grade AI agents. It's designed to seamlessly integrate AI into existing business applications with a strong focus on security, modularity, and structured planning, using "skills" and "planners" to create predictable behavior.
Selling Points:
Enterprise-Grade Focus: Built with security, reliability, and integration into existing systems as top priorities.
Structured "Skills" & "Planners": Offers a more predictable and controllable way to define an agent's capabilities and goals.
Deep Microsoft Ecosystem Integration: Designed to work smoothly within an enterprise environment that relies on Microsoft technologies.
Choose it when:
- You need to integrate AI agents into existing enterprise systems with a focus on security and reliability.
- Your developers want to use “skills” and “planners” to create highly structured and predictable agent behavior.
Don't choose it when:
You need a production-ready tool today; many of its features are still considered "experimental," so a more mature framework might be safer for critical applications.
Collaborative & Low-Code Platforms: If You Don't Have a Technical Team
These options are designed for teams without dedicated developers. They use more visual, intuitive, or manager-friendly approaches to build and deploy AI agents.
1CrewAI
CrewAI simplifies the creation of multi-agent systems by framing it as a project management task. You define roles for your AI agents (e.g., 'Researcher,' 'Writer') and assign them tasks in plain English. The "crew" then works together sequentially to achieve the final goal.

Selling Points:
Simple, Human-Readable Logic: The process is defined like a project plan, making it easy for non-programmers to understand and manage.
Intuitive Role-Based Design: Its core concept of "roles" and "tasks" is instantly familiar to any manager.
Accessible for Non-Developers: While it requires some setup, its logic is far more accessible than code-heavy alternatives.
Choose it when:
- You want to build and manage a multi-agent system using natural language.
- You're familiar with a "team collaboration" model and want to apply it to AI automation.
- Your task requires multiple agents to work together, but you don't want to deal with the underlying code.
Don't choose it when:
You only need to build a simple, single-agent chatbot.
2Botpress
If your primary goal is building a chatbot for sales, support, or as a website assistant, Botpress is the "Canva" of conversational AI. It's a powerful visual platform that lets you build, test, and deploy sophisticated chatbots using a drag-and-drop interface.
Selling Points:
Visual Drag-and-Drop Editor: Allows non-technical users to build complex conversation flows intuitively.
Fast Prototyping & Deployment: Go from an idea to a functioning chatbot on your website in record time.
Empowers Non-Technical Teams: Enables marketing, sales, or support teams to own and update their bots without developer dependency.
Choose it when:
- Your business needs a conversational AI agent (e.g., a customer service bot, a Q&A system).
- You want to rapidly prototype and deploy your agent using a low-code/no-code approach.
Don't choose it when:
- The AI agent you need is not conversation-based and focuses on backend workflow automation.
Conceptual Frameworks: If You Just Want to Experiment
This category is for AI enthusiasts and researchers who want to explore the future of autonomous agents, not for building production-ready business tools.
1Auto-GPT
Auto-GPT was the viral project that introduced the world to the idea of a fully autonomous AI agent. You give it a high-level goal, and it attempts to figure out all the steps—from planning to execution—entirely on its own.
Selling Points:
Pioneered Autonomous Agents: A landmark project for understanding the potential and challenges of AI autonomy.
Demonstrates Fully Autonomous Goal-Seeking: Shows how an AI can attempt to reason, plan, and act on its own.
Excellent for Research & Learning: Its flaws and unpredictability make it a fascinating subject for study.
Choose it when:
- You are a researcher or AI enthusiast who wants to explore the boundaries of AI agent capabilities.
Don't choose it when:
- You want a stable, reliable tool that can create business value. Its instability makes it.
Comparison Table
Based on our detailed look at each framework, you should now have a solid understanding of their individual strengths. To help you quickly compare them, here's a summary table that puts all the key details in one place.
| Framework Name | Ideal User | Core Use Case (One Sentence) | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|
| LangChain | Developers | Building highly customized AI applications. | Unmatched flexibility and the largest ecosystem. |
| LangGraph | Developers | Precisely controlling complex, non-linear workflows. | Graph architecture for high reliability and control. |
| Microsoft AutoGen | Developers | Automating multi-agent team collaboration. | Agents solve problems by "talking" to each other. |
| OpenAI Agents SDK | Developers | Quickly building multi-agent applications within the OpenAI ecosystem. | A lightweight, official toolkit for rapid development. |
| Semantic Kernel | Developers | Integrating AI into enterprise-grade applications. | Structured planning, security, and deep Microsoft integration. |
| CrewAI | Business Managers, Non-Technical Users | Orchestrating AI agent teams using natural language. | Simplifies complex orchestration into a team management model. |
| Botpress | Non-Technical Users | Rapidly building conversational AI applications. | A visual, low-code, drag-and-drop editor. |
| Auto-GPT | Researchers, Enthusiasts | Exploring the boundaries of autonomous AI. | Pioneers autonomous, goal-driven task planning. |
How to Choose the Right AI Agent Framework
When selecting an AI agent framework, there are a few key criteria to consider. Depending on your specific needs, the right option for you may vary:
- Specific business needs: Identify the 'core'goal you're aiming for; is it a chatbot, workflow automation, research assistant, etc.
- Task complexity: For your goal, do you need a linear, 'simpler'workflow? Or do you require custom, complex branching multi-agent systems?
- Integration requirements: What tools do you need to integrate your AI agents with, if any? Do you need to connect to specific APIs, internal databases, or enterprise systems?
- Scalability: Will you need to grow agent size and capability over time?
- No-code or code-heavy?: Do you or your team require visual no-code builders, or do you prefer code-heavy customization?
Here are a few examples to identify matching frameworks for your workflows:
- Customer service chatbot (Botpress): Easy to use, no-code visual builder for non-technical users and seamless conversation design.
- Research & multi-step planning (AutoGen/CrewAI): Allows multi-agent collaboration and task division.
- AI Agent ideation & testing (AutoGPT): Best for quickly prototyping and experimenting with new automation workflows before committing to a full build.
- Complex workflows & integrations (LangChain/LangGraph): Ideal for advanced pipelines & branching workflows that require reasoning across multiple tools, APIs, or databases.
Best Practices & Tips
When selecting a framework, don't get lost in the technical jargon. Instead, focus on your business goals. Here are a few key criteria to consider:
- Specific business needs: What is the core goal you're aiming for? A chatbot, workflow automation, or a research assistant?
- Task complexity: Do you need a simple, linear workflow, or a complex, multi-agent system with branching paths?
- Integration requirements: What tools, databases, or APIs do you need to connect your agent to?
- Scalability: Will you need to grow your agent's size and capabilities over time to handle more data or users?
- No-code or code-heavy?: Do you or your team prefer visual, no-code builders or code-heavy customization?
By answering these questions, you can quickly narrow down your options.
Bonus: Get Started with AI Workflow on GoInsight.ai
You've learned how frameworks help you build a powerful, intelligent AI agent. But once your agent is built, what's next? An agent can summarize customer feedback, but without a workflow, it's just a powerful tool sitting alone. It needs to be connected to your business.
This is where GoInsight.ai comes in.
Our platform helps you go beyond building the agent by putting it to work inside an end-to-end workflow. For example, you can build a workflow that automatically summarizes all your customer feedback.
- The workflow is triggered every day by new data from a tool like Salesforce or Zendesk.
- Our platform sends that data to your AI agent for analysis and summarization.
- Finally, the platform automatically sends a concise summary to your Slack channel or email inbox.
All in all, with GoInsight.ai, you're not just building a smart agent—you're building a smart, automated workflow that connects your agents to all your business tools and data, saving you time and transforming how your work gets done.
Conclusion
Building AI agents can seem hard, but frameworks make it easy to begin. They are not just for experimentation; they are practical solutions that reshape how work gets done, offering long-term productivity gains that make the investment of time and effort well worth it. Armed with the knowledge of what these frameworks are and how to choose one, the only thing left to do is to start building. Don't wait. Choose a framework and start building your first automation today.






Leave a Reply.